JavaEE
1.SpringBoot
1.Rest风格
1.1Rest
1.1.1 Rest简介
- Rest 表现形式状态转换
传统风格
Rest风格
http://localhost/user/1 (查询单数,删除用户信息)
http://localhost/user (查询复数,添加,修改用户信息)
优点
隐藏资源访问行为
书写简化
1.1.2 地址栏传参模式—-参数配置
- method = RequestMethod.GET 查询
- method = RequestMethod.POST 保存
- method = RequestMethod.DELETE 删除
- method = RequestMethod.HEAD
- method = RequestMethod.PUT 更新
- method = RequestMethod.OPTIONS
- method = RequestMethod.PATCH
- method = RequestMethod.TRACE
package top.wabisabifag.controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
@Controller
public class UserController {
@RequestMapping(value = "/users",method = RequestMethod.POST)
@ResponseBody
public String save(){
System.out.println("user save...");
return "{'module':'user save'}";
}
/**
* {id} 代表请求格式,对应方法的传参值
* @PathVariable 指定 id 的所取值,url地址传给方法
*/
@RequestMapping(value = "/users/{id}",method = RequestMethod.DELETE)
@ResponseBody
public String delete(@PathVariable Integer id){
System.out.println("user delete..."+id);
return "{'module':'user delete'}";
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/users",method = RequestMethod.PUT)
@ResponseBody
public String update(@RequestBody User user){
System.out.println("user update..."+user);
return "{'module':'user update'}";
}
/*
* @RequestMethod.GET 专门查询语句
*/
@RequestMapping(value = "/users/{id}",method = RequestMethod.GET)
@ResponseBody
public String getById(@PathVariable Integer id){
System.out.println("user getById..."+id);
return "{'module':'user getById'}";
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/users",method = RequestMethod.GET)
@ResponseBody
public String getAll(){
System.out.println("user getAll...");
return "{'module':'user getAll'}";
}
}总结:
区别
@RequestParam 用于接受 url 地址传参或表单传参
@RequestBody 用于接受json数据
@PathVariable 用于接收路径参数,使用 {name} 描述路径参数
应用
后期开发,发送请求超过一个参数,以json格式,@RequestBody 应用为主
如果发送非json格式数据,选用@RequestParam 接收请求参数
采用RESTful进行开发,当参数较少时,采用@PathVariable 接收请求路径变量,传递 id 值
1.1.3 Rest快速开发
package top.wabisabifag.controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
@RestController
@ResponseBody
//@RestController
@RequestMapping("/users")
public class UserController {
@PostMapping
public String save(@RequestBody User user){
System.out.println("user save...");
return "{'module':'user save'}";
}
/**
* {id} 代表请求格式,对应方法的传参值
* @PathVariable 指定 id 路径 的 所取值
*/
@DeleteMapping("/{id}")
public String delete(@PathVariable Integer id){
System.out.println("user delete..."+id);
return "{'module':'user delete'}";
}
@PutMapping
public String update(@RequestBody User user){
System.out.println("user update..."+user);
return "{'module':'user update'}";
}
/*
* @RequestMethod.GET 专门查询语句
*/
@GetMapping("/{id}")
public String getById(@PathVariable Integer id){
System.out.println("user getById..."+id);
return "{'module':'user getById'}";
}
@GetMapping
public String getAll(){
System.out.println("user getAll...");
return "{'module':'user getAll'}";
}
}主要点:
简化
- @RestController 等价 @ResponseBody < < ==== > > @RestController (目的:省略重复)
- value = “/users” 省略:value 但不能省略传递的 {name} 值
- method = RequestMethod. { } @…Mapping代替 单值 和 POJO值 的传值方式
- @PathVariable 单值传输
- @RequestBody POJO值传输
2.基础配置
2.1 属性配置
SpringBoot Appilcation.properties文档地址
2.1.1 Springboot 多种属性配置(文件优先级递减)
- .properties
- server.port=80
- .yml
- server:
port: 80
- server:
- .yaml
- server:
port: 80
- server:
1.yml格式
多层级属性名
a: b: C: 1145137数组属性名
likes: - games - foods - books # 缩略模式 likes:[games,foods,books]对象数组属性名
users: - name: zhangsan age: 18 - name: Jhon age: 16 # 缩略模式 users:[{name:zhangsan,age:18},{name:Jhon,age:16}]
2.数据读取
@value("${users.name}")
private String name;
@value("${likes[1]}")
private String games;
@value("${users[1].name}")
private String name;baseDir: c:\windows
# 使用 ${value} 引用数据
tempDir: ${baseDir}\temp属性值(value)用 “"转义字符 的会不显示
使用 “spring\boot\text.txt”
3.封装数据
全配置封装
//自动装配 @Autowired private Environment environment; environment.getProperty("users[0].name");针对性封装
spring: datasource: url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8&useSSL=false username: root password: 123456 driver: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver# 1.创建类,封装数据 package top.wabisabifag.POJO; import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; # 2.Spring加载数据对象,告诉Spring加载信息 @Data @Component @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource") public class MyDataSource { private String url; private String username; private String password; private String driver; }# 3.使用Spring获取的信息 @Autowired private MyDataSource myDataSource;
2.1.2 修改服务器端口
# 1.配置服务器端口
server.port=80
# 2.修改Spring启动的banner
# 关闭Spring Logo
spring.main.banner-mode=off
# 将text,png等文件转化为二维图
#spring.banner.image.location=1.png
# 3.控制日志
# 输出日志级别
#logging.level.root=debug
# 在出错时输出日志
logging.level.root=error3.第三方技术整合
1.JUnit
package top.wabisabifag.dao.Impl;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
import top.wabisabifag.dao.BookDao;
/* 3.接受Spring管理 */
@Repository
public class BookDaoImpl implements BookDao {
@Override
public void save() {
System.out.println("BookDao testing");
}
}package top.wabisabifag.test;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import top.wabisabifag.dao.BookDao;
/* 4.获取Spring管理声明 */
@SpringBootTest
public class SpringBootJUnitApplicationTests {
/*1.注入测试对象*/
@Autowired
private BookDao bookDao;
/*2.执行测试方法*/
@Test
void contextLoads(){
bookDao.save();
}
}当test 测试路径无法对应java 源代码路径
@SpringBootTest(classes = BookDaoImpl.class)来申明源码
@SpringBootTest(classes = BookDaoImpl.class)@RunWith(设置运行器)
@ContextConfiguration(class = .... ) //配置引导类或配置类
- ContextConfiguration 用于在当前包下查找声明类
2.MybatisPlus
<dependency>
<groupId>com.baomidou</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-plus-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>3.4.2</version>
</dependency>#配置MP相关数据库名称
mybatis-plus:
global-config:
db-config:
table-prefix: tb_package top.wabisabifag.dao;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.core.mapper.BaseMapper;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Mapper;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Select;
import top.wabisabifag.POJO.Book;
@Mapper // 继承 BaseMapper
public interface BookDao extends BaseMapper {
public void save();
@Select("select * from smbms_user where userid = #{id} ")
public Book getById(int id);
}package top.wabisabifag.config;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.annotation.DbType;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.extension.plugins.MybatisPlusInterceptor;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.extension.plugins.inner.PaginationInnerInterceptor;
import org.mybatis.spring.annotation.MapperScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
@MapperScan("top.wabisabifag.dao")
public class MybatisPlusConfig {
// 配置分页设置类
@Bean
public MybatisPlusInterceptor mybatisPlusInterceptor() {
MybatisPlusInterceptor interceptor = new MybatisPlusInterceptor();
interceptor.addInnerInterceptor(new PaginationInnerInterceptor(DbType.MYSQL));
return interceptor;
}
}package top.wabisabifag.test;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import top.wabisabifag.dao.BookDao;
import top.wabisabifag.dao.Impl.BookDaoImpl;
@SpringBootTest(classes = BookDaoImpl.class)
public class SpringBootJUnitApplicationTests {
/*1.注入测试对象*/
@Autowired
private BookDao bookDao;
/*2.执行测试方法*/
@Test
void contextLoads(){
bookDao.save();
bookDao.getById(1);
}
@Test
void contextLoadsPlus(){
System.out.println(bookDao.selectById(2));
}
}4.Lombok
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
</dependency>package top.wabisabifag.domain;
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
import lombok.ToString;
@Data // @Getter @Setter
@NoArgsConstructor // 无参构造
@AllArgsConstructor // 有参构造
@ToString
public class User {
private int id;
private String userCode;
}主要:
- @Getter @Setter 等价于 @Data
5.Druid
------pom 获取Druid依赖------
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>druid-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>1.1.23</version>
</dependency>
-------配置--------
通用配置:
spring:
datasource:
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/smbms_db?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8&useSSL=false
username: root
password: 123456
driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
整合配置:
spring:
datasource:
druid:
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/smbms_db?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8&useSSL=false
username: root
password: 123456
driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver2.SSMP整合案例
- 实体类开发 使用Lombok 快速制作实体类
- Dao 开发 整合MyBatisPlus ,制作数据层测试类
- Service 开发 基于MyBatisPlus 进行增量开发,制作业务层测试类
- Controller 开发 基于Restful 开发,使用PostMan 测试接口功能
- Controller 开发 前后端开发协议制作
- 页面开发 基于VUE,Element制作,前后端联,页面数据处理
- CRUD 分页,查询操作
- 项目异常处理
- 按条件查询 页面功能调整,Controller修正功能,Service修正功能
SMMP源代码
3.SpringBoot维护
1.工程运行
1.Windows jar 包执行
1. 执行jar 包: java -jar packageName
2. 查询端口: netstat -ano
3. 查询指定端口: netstat -ano |findstr "端口号"
4. 根据进程PID 查询进程名称: tasklist |findstr "进程号PID号"
5. 根据PID 杀死任务: tasklist /F /PID "进程PID号"
6. 根据进程名称杀死任务: taskkill -f -t -im "进程名称" 进程名称有多个相同的2.Linux jar 包执行
1. 启动后端: nohup java -jar jarPackageName > server.log 2>&1 &3.临时属性配置
执行jar 包: java -jar packageName –server.port=8080 –spring.datasouce.druid.password=root
@SpringBootApplication @MapperScan("top.wabisabifag.dao")/*使用@MapperScan可以指定要扫描的Mapper类的包的路径*/ @ComponentScan(basePackages={"top.wabisabifag"}) public class application { public static void main(String[] args) { // 线程安全问题 // SpringApplication.run(application.class,args); // 不接受外部临时参数 SpringApplication.run(application.class); } }application.yml 的双配置
文件位置: 1. web/springboot.jar/resources/application.yml
2. web/springboot.jar/resources/config/application.yml
3. web/application.yml
4. web/config/application.yml
重 复: 文件优先级配置高覆盖低的;
不重复: 互不干扰;
权限等级: 逐级上升(4 > 3 > 2 > 1)
文件内config/ .yml > 文件外 .properties
4.多环境开发
1. YAML
# 一、应用环境
spring:
profiles:
active: pro
---
# 二、设置环境
# 1. 公共环境
# 2. 自定义环境
spring:
profiles: pro
server:
port:80
---
spring:
profiles: dev
server:
port:81
---
spring:
config:
activate:
on-profiles: test
server:
port:82
YAML 弊端
1.— : 分割线是格式需求
2.容易暴露信息,安全有问题
YAML 优化
生成配置文件:
application-dev.yml
application-pro.yml
application-test.yml
可以独立配置文件定义环境;
独立配置文件便于线上系统维护更新并保障系统安全性;
2. properties
- 文件内容格式
spring.profiles=pro server.port=80 --- spring.profiles=dev server.port=81 --- spring.profiles=test spring.profiles=82 - 生成配置文件:
application-dev.properties
application-pro.properties
application-test.properties
3. 独立的功能配置文件
- 根据功能 对配置文件的信息拆分
- application-devDB.yml
- application-devRedis.yml
- application-devMVC.yml
- application.yml 中使用include 属性在激活指定环境 条件下,同时对多环境进行加载
- application.yml 后加载
spring: profiles: active: dev include: devDB,devRedis,devMVC
- application.yml 后加载
优化 include 无法动态更改问题
+ application.yml 前加载
SpringBoot 2.4.X 后:
spring:
profiles:
active: dev
group:
"dev": devDB,devRedis,devMVC
"pro": proDB,proRedis,proMVC
"test": testDB,testRedis,testMVC4. 多环境开发控制(Maven)
<!--设置多环境-->
<profiles>
<profile>
<id>env_dev</id>
<properties>
<profile.active>dev</profile.active>
</properties>
<!--设置默认启动-->
<activation>
<activeByDefault>true</activeByDefault>
</activation>
</profile>
<profile>
<id>env_pro</id>
<properties>
<profile.active>pro</profile.active>
</properties>
</profile>
</profiles>spring:
profiles:
<!-- 使用Maven 的环境配置的格式 "@....@" -->
active: @profile.active@
group:
"dev": devDB,devRedis,devMVC
"pro": proDB,proRedis,proMVC
"test": testDB,testRedis,testMVC- ieda 对Maven 环境的更改无法生效,需要手动编译compile
5. 日志
1. 日志设置
- 代码中使用日志工具记录日志
@RestController @RequestMapping("/users") @CrossOrigin public class UserController { private static final Logger log = (Logger) LoggerFactory.getLogger(UserController.class); @GetMapping("/{id}") public User getById(@PathVariable Integer id){ // application.yml debug:true log.debug("debug..."); log.info("info..."); log.warning("warn..."); log.error(); log.fatal(); return userService.getById(id); } } - 设置日志级别
# 开启debug模式,输出调试信息,常用于检查系统运行状况 debug: true # 设置日志级别 root表示根节点,整体应用日志级别 logging: level: root: error # 设置某包的日志级别 top.wabisabifag.controller: debug # 设置分组,对某个祖设置日志级别 enable:warn
2. 日志工具 (动态和继承)
设置日志对象
package top.wabisabifag.controller.Logger; import org.slf4j.Logger; import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory; import top.wabisabifag.controller.UserController; public class LoggerClass { private Class clazz = null; public static Logger log; public LoggerClass(){ clazz = this.getClass(); log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(UserController.class); } }日志工具引入控制层
package top.wabisabifag.controller.Logger; import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*; @Slf4j // 开启日志 @RestController @RequestMapping("/users") @CrossOrigin public class UserController3 extends LoggerClass { @GetMapping("/{id}") public String getById(@PathVariable Integer id){ log.debug("debug..."); log.info("info..."); log.warning("warn..."); log.error("error..."); log.fatal(); return "springboot is running... 2"; } }
3. 日志输出格式
- 控制台日志输出
# 日志配置 logging: level: root: error pattern: console: "%d %clr(5p) --- [%16t] %clr(%-40.40c){red} :%m %n"
- d 日期
- p 信息的级别
- %clr(%5p) 颜色设置
- %5p 占据的长度
- [%16 t] 运行的文件
- %-40 左对齐
- .40c 截断后,容纳40长度
- m 消息
- n 换行
- 日志记录
# 日志配置 logging: level: root: error # 控制台日志输出 pattern: console: "%d %clr(5p) --- [%16t] %clr(%-40.40c){red} :%m %n" # 日志文件记录 file: name: server.log # 日志分期记录 logback: rollingpolicy: max-file-size: 3KB file-name-pattern: server.%d{yyyy-MM-dd}.%i.log # 输出格式: server.2023-09-20.0.log
4.SpringBoot应用开发
1. 热部署
1. 热部署依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-devtools</artifactId>
</dependency>- 手动配置:在IEDA激活热部署: Ctrl + F9
- 自动配置:生命周期compile
2. 热部署范围
spring:
datasource:
druid:
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/smbms
username: root
password: 123456
driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
# 设置不参与热部署的文件与文件夹
# 默认不重启:
# /META-INF/maven /META-INF/resources /resources /static /public /templates
devtools:
restart:
# 排除
exclude: static/**,public/**,config/application.yml3. 关闭热部署
热部署功能只适用于 开发环境
1.设置文件层级控制
spring:
datasource:
druid:
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/smbms
username: root
password: 123456
driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
# 设置不参与热部署的文件与文件夹
# 默认不重启:
# /META-INF/maven /META-INF/resources /resources /static /public /templates
devtools:
restart:
# 排除
exclude: static/**,public/**,config/application.yml
# 开关 受到权限层级影响
enable: true2. 系统层级覆盖控制
package top.wabisabifag;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
public class SSMPApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 系统层级覆盖热部署功能
System.setProperty("spring.devtools.restart.enabled","false");
SpringApplication.run(SSMPApplication.class);
}
}2. Swagger生成WebAPI文档
Swagger类似Postman,提供文档传输的可视化页面
1.部署应用Swagger
<!--Swagger生成Web API文档-->
<dependency>
<groupId>io.springfox</groupId>
<artifactId>springfox-swagger2</artifactId>
<version>3.0.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.springfox</groupId>
<artifactId>springfox-swagger-ui</artifactId>
<version>3.0.0</version>
</dependency>spring:
mvc:
pathmatch:
matching-strategy: ant_path_matcherpackage top.wabisabifag.config;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import springfox.documentation.builders.ApiInfoBuilder;
import springfox.documentation.builders.PathSelectors;
import springfox.documentation.builders.RequestHandlerSelectors;
import springfox.documentation.service.ApiInfo;
import springfox.documentation.spi.DocumentationType;
import springfox.documentation.spring.web.plugins.Docket;
import springfox.documentation.swagger2.annotations.EnableSwagger2;
@Configuration
@EnableSwagger2
public class Swagger2Config {
/*
* 可视化测试页面:http://localhost:8080/swagger-ui.html
*/
@Bean
public Docket createRestApi(){
return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2)
.apiInfo(apiInfo())
.select()
.apis(RequestHandlerSelectors.basePackage("top.wabisabifag"))
.paths(PathSelectors.any()).build();
}
// API 文档页面显示信息
private ApiInfo apiInfo(){
return new ApiInfoBuilder()
.title("演示项目API")
.build();
}
}
Swagger的文档页面地址: http://localhost:8080/swagger-ui.html
2. 第三方Bean 属性绑定(configuration)
1. Bean 属性绑定
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>druid</artifactId>
<version>1.1.23</version>
</dependency>
<!--springboot第三方配置绑定-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-configuration-processor</artifactId>
</dependency>servers:
ipAddress: 192.168.0.1
port: 2345
timeout: -1
datasource:
driverClassName: com.mysql.jdbc.Driverpackage top.wabisabifag.config;
import lombok.Data;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
//@Component // 受Spring接管 加载为Bean 和 @EnableConfigurationProperties 冲突
@Data
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "servers") // 映射配置设置
public class ServertConfig {
private String ipAddress;
private int port;
private long timeout;
}package top.wabisabifag;
import com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.EnableConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import top.wabisabifag.config.ServertConfig;
@SpringBootApplication
/* 自动加载配置类为Bean 和 @Component 冲突
开启属性绑定 并 设定对应的类 */
@EnableConfigurationProperties(ServertConfig.class)
public class SpringBootConfigurationApplication {
/* 第三方配置类 Bean 已经加载 但是没有配置属性值
可配置自定义 和 第三方 的 配置属性值绑定
1.报错: 注解没有配置 加载 spring-boot-configuration-processor 依赖
2.宽松绑定: 配置文件驼峰命名时,此处不用遵从命名规范 */
@Bean
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "datasource")
public DruidDataSource dataSource(){
DruidDataSource dataSource = new DruidDataSource();
//dataSource.setDriverClassName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
return dataSource;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ConfigurableApplicationContext ctx = SpringApplication.run(SpringBootConfigurationApplication.class,args);
// ../config/ServerConfig 类
ServertConfig bean = ctx.getBean(ServertConfig.class);
System.out.println(bean);
// 配置值
DruidDataSource dataSource = ctx.getBean(DruidDataSource.class);
// 获取懒加载的配置属性
System.out.println(dataSource);
// 设置的值 普通类对象
System.out.println(dataSource.getDriverClassName());
}
}2. 宽松绑定
- @ConfigurationProperties 适配多种命名模式
- 驼峰: ipAddress
- underLine ip_adderess
- 矢量 (烤肉串) ip-address (主要适应应用)
- 常亮 IP_ADDRESS
- @Value 数据绑定支持 驼峰
@SpringBootTest class application{ @Value("${servers.ipAddress}") private String msg; @Test void contextLoads(){ System.out.println(msg); } }
3. 常量计量单位应用(jdk版本:8)
servers:
ipAddress: 192.168.0.1
port: 2345
timeout: -1
# 数据存储时间,服务器超时时间: 毫秒
serverTimeOut: 3
# 数据存储单位: Byte
dataSize: 10package top.wabisabifag.config;
import lombok.Data;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.boot.convert.DataSizeUnit;
import org.springframework.boot.convert.DurationUnit;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.util.unit.DataSize;
import org.springframework.util.unit.DataUnit;
import java.time.Duration;
import java.time.temporal.ChronoUnit;
//受Spring接管 加载为Bean 和 @EnableConfigurationProperties 冲突
//@Component
@Data
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "servers") // 映射配置设置
public class ServertConfig {
private String ipAddress;
private int port;
private long timeout;
@DurationUnit(ChronoUnit.HOURS) // 时间单位自定义
private Duration serverTimeOut;
@DataSizeUnit(DataUnit.GIGABYTES) // 数据存储单位自定义
private DataSize dataSize;
}4. 数据校验
<!--数据校验 JSR303规范 接口-->
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.validation</groupId>
<artifactId>validation-api</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--校验框架 实现-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.hibernate.validator</groupId>
<artifactId>hibernate-validator</artifactId>
</dependency>package top.wabisabifag.config;
import lombok.Data;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.boot.convert.DataSizeUnit;
import org.springframework.boot.convert.DurationUnit;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.util.unit.DataSize;
import org.springframework.util.unit.DataUnit;
import org.springframework.validation.annotation.Validated;
import javax.validation.constraints.Max;
import javax.validation.constraints.Min;
import javax.validation.constraints.NotEmpty;
import java.time.Duration;
import java.time.temporal.ChronoUnit;
@Data
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "servers") // 映射配置设置
@Validated //2. 对Bean属性注入校验
public class ServertConfig {
private String ipAddress;
// 3. 设置规则
@Max(value = 8888,message = "端口号不能超过 8888")
@Min(value = 888,message = "端口号不能超过 888")
//@NotEmpty
private int port;
private long timeout;
@DurationUnit(ChronoUnit.HOURS)// 时间单位自定义
private Duration serverTimeOut;
@DataSizeUnit(DataUnit.GIGABYTES)// 数据存储单位自定义
private DataSize dataSize;
}5. 进制数据转换
- 报错: 密码错误
datasource:
driverClassName: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
password: 0127@SpringBootTest
class application{
@Value("${datasource.password}")
private String password;
@Test
void contextLoads(){
System.out.println(password); // 输出值: 87
}
}- 原因:
- String 类型接收的 password
- datasource.password: 0127 。 为0 开头的8进制 且只有数字,没有用”” 束缚。 编译为十进制为:87
6. 测试
1. 加载测试专用属性
test:
prop: testValuepackage top.wabisabifag;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
//@SpringBootTest(properties = {"test.prop=testValue1"}) // 添加临时的数组属性
@SpringBootTest(properties = {"test.prop=testValue1"},args = {"--test.prop=testValue2"})
public class PropertiesAndArgsTest {
@Value("${test.prop}")
private String msg;
@Test
public void testProperties(){
/* 2.7.x 层级权限 properties > args
2.5.x 层级权限 properties < args
*/
System.out.println(msg);
}
}1. 局部配置导入
package top.wabisabifag.config;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
public class MsgConfig {
@Bean
public String msg(){
return "bean msg";
}
}package top.wabisabifag;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Import;
import top.wabisabifag.config.MsgConfig;
@SpringBootTest
@Import({MsgConfig.class}) // 加载当前测试类专用的配置
public class ConfigurationTest {
@Autowired
private String msg;
@Test
public void testConfiguration(){
System.out.println(msg);
}
}- 加载测试临时属性应用于小范围测试环境
2. Web 环境模拟测试
package top.wabisabifag.controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/books")
public class BookController {
@GetMapping
public String getById(){
System.out.println("getById is running ...");
return "springboot";
}
/*json 数据的响应体*/
@GetMapping
@ResponseBody
public String finall(){
return "{\"name\" : Web测试成功}";
}
}package top.wabisabifag;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.autoconfigure.web.servlet.AutoConfigureMockMvc;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.mock.web.MockServletContext;
import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.MockMvc;
import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.ResultActions;
import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.ResultMatcher;
import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.request.MockHttpServletRequestBuilder;
import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.request.MockMvcRequestBuilders;
import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.result.ContentResultMatchers;
import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.result.HeaderResultMatchers;
import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.result.MockMvcResultMatchers;
import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.result.StatusResultMatchers;
// 模拟端口启动Web 环境===> 随机端口
@SpringBootTest(webEnvironment = SpringBootTest.WebEnvironment.RANDOM_PORT,classes = {MockServletContext.class })
// 虚拟调用MVC 注解
@AutoConfigureMockMvc
public class WebTest {
// 引入MockMvc类型对象
@Autowired
private MockMvc mvc;
// 调用 MockMvc 执行Controller 层功能
@Test
public void testWeb() throws Exception {
MockHttpServletRequestBuilder builder = MockMvcRequestBuilders.get("/books");
// 执行对应请求
ResultActions actions = mvc.perform(builder);
}
@Test
public void testStatus() throws Exception {
/*http://localhost:8080/books 创建虚拟请求,当前访问 /books */
MockHttpServletRequestBuilder builder = MockMvcRequestBuilders.get("/books");
/*这里需要抛出异常 获取返回值*/
ResultActions actions = mvc.perform(builder);
/*1 .status()响应状态 匹配*/
// 定义本次调用的预期值
StatusResultMatchers status = MockMvcResultMatchers.status();
// 预计本次调用时成功的状态: 200
ResultMatcher ok = status.isOk();
// 添加预期值到本次调用过程中进行匹配
actions.andExpect(ok);
/*2 .content()响应体 匹配*/
ContentResultMatchers content = MockMvcResultMatchers.content();
/* 1. content.string*/
ResultMatcher stringData = content.string("Web测试成功");
actions.andExpect(stringData);
/* 2. content.json*/
ResultMatcher jsonData = content.json("{\"name\":Web测试成功}");// controller return 的结果
actions.andExpect(jsonData);
/*3 .header()响应头 匹配*/
HeaderResultMatchers header = MockMvcResultMatchers.header();
ResultMatcher contentType = header.string("Content-Type", "text/plain;charset=UTF-8");
actions.andExpect(contentType);
}
}3. 业务层数据测试事物回滚
#在application.properties/或者application.yml文件中没有添加数据库配置信息.
# url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/smbms?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8&useSSL=false
spring:
datasource:
druid:
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/smbms
username: root
password: 123456
driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
#配置MP相关数据库名称
mybatis-plus:
configuration:
# 日志
log-impl: org.apache.ibatis.logging.stdout.StdOutImpl
global-config:
db-config:
table-prefix: smbms_
id-type: autopackage top.wabisabifag.domain;
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Data;
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
public class Book {
private int id;
private String name;
private String type;
private String description;
}package top.wabisabifag.dao;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.core.mapper.BaseMapper;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Mapper;
import top.wabisabifag.domain.Book;
@Mapper
public interface BookDao extends BaseMapper<Book> {
}package top.wabisabifag.service;
import top.wabisabifag.domain.Book;
public interface BookService {
public boolean save(Book book);
}package top.wabisabifag.service.impl;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import top.wabisabifag.dao.BookDao;
import top.wabisabifag.domain.Book;
@Service
public class BookServiceImpl {
@Autowired
private BookDao bookDao;
public boolean save(Book book){
return bookDao.insert(book) > 0;
}
}package top.wabisabifag;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.test.annotation.Rollback;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
import top.wabisabifag.domain.Book;
import top.wabisabifag.service.BookService;
@SpringBootTest
@Transactional // 事务注解: 停止事务提交,自动回滚 [内涵 @Rollback(true)]
//@Rollback(false) 测试时,提交事物更改值
public class BookDaoTest {
@Autowired
private BookService bookService;
@Test
public void testSave(){
Book book = new Book(1,"name","type","description");
bookService.save(book);
}
}- 不做数据留痕,不做垃圾数据,脏数据保存
4. 测试用例数据设定
1. 测试用例设定随机数据
#在application.properties/或者application.yml文件中没有添加数据库配置信息.
# url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/smbms?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8&useSSL=false
spring:
datasource:
druid:
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/smbms
username: root
password: 123456
driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
#配置MP相关数据库名称
mybatis-plus:
configuration:
# 日志
log-impl: org.apache.ibatis.logging.stdout.StdOutImpl
global-config:
db-config:
table-prefix: smbms_
id-type: auto
# 测试用例设定随机数据
testcase:
book:
id: ${random.int(0,10)} # 自定义随机范围
name: Wabisabifag${random.value} # 数据可拼接
uuid: ${random.uuid}
publishTome: ${random.long}package top.wabisabifag.domain;
import lombok.Data;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
@Data
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "testcase.book")
public class BookCase {
private int id;
private String name;
private String uuid;
private long publishTime;
}package top.wabisabifag;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import top.wabisabifag.domain.BookCase;
@SpringBootTest
public class BookDaoTest {
@Autowired
private BookCase bookCase;
public void testBookCase(){
System.out.println(bookCase);
}
}7. 数据层解决方案
1. SQL
数据层解决方案:
数据源 持久化 数据库
Druid MyBatis-Plus MySql
Hikari MyBatis H2
JDBCTemplate
1. 数据源配置(DruidDataSource)
- SpringBoot提供的3种内嵌的数据源对象
- HiKariCP
- Tomcat 提供 DataSource
- Commons DBCP
spring: datasource: url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/smbms # 进一步配置 hikari、 tomcat 、dbcp2 数据实现 hikari: username: root password: 123456 driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver maximum-pool-size: 50 # 最大连接池数量
2. 数据持久化(jdbcTemplate)
1. JDBCTemplate 配置
spring:
jdbc:
template:
query-timeout: -1 # 查询超时时间
max-rows: 500 # 最大行数
fetch-size: -1 # 批处理数量3. 数据库(MySQL)
- SpringBoot提供的3种内嵌的数据库
- 内存级别数据库: 基于Java开发,可以在内存中启动运行,方便测试
- H2
- HSQL
- Derby
<!--H2 数据库依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.h2database</groupId>
<artifactId>h2</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starte-data-jpa</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starte-web-jpa</artifactId>
</dependency>#在application.properties/或者application.yml文件中没有添加数据库配置信息.
spring:
# h2 数据库配置
h2:
console:
path: /h2
# 仅用于开发阶段 安全风险巨大
enabled: true
# H2 数据库初始化时需要配置数据源
# 格式同页面提供的数据源样式
datasource:
druid:
url: jdbc:h2:~/test
username: root
password: 123456
# 可以省略, 设置后必须保证可访问
driver-class-name: org.h2.Driver
# 配置服务器端口
server:
port:
80
servlet:
context-path: /1. 访问H2 数据库服务页面
- localhost://h2
2. NoSQL
- 主要常见的NoSQL 解决方案 (常在Linux 系统中部署安装)
1. Redis
- Redis 是一款 Key-Value 存储结构的内存级 NoSQL 数据库
- 支持多种数据存储格式
- 支持持久化
- 支持集群
1. Redis基础操作
启动安装
# 服务端启动命令 声明参数 redis-sercer.exe redis.windows.conf (如果服务端无法启动,先执行客服端启动命令。这里shutdown就是为了关闭这个版本的redis默认创建的服务,服务可以在任务管理中找到) # 客服端启动命令 redis-cli.exe shutdownRedis 存储获取 值
# 存储 key value set name wabisabifag # 获取 get name # 查询所有数值 keys * # 清屏 clear # 设置多个嵌套值 hset keya a1 aa1 hset keya a2 aa2 hget keya a1 # "aa1" hget keya a2 # "aa2"
2. Redis整合
<dependencies>
<!--Nosql整合数据库-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>spring:
redis:
host: localhost
port: 6379package top.wabisabifag;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.StringRedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.ValueOperations;
@SpringBootTest
public class Application {
// 以对象作为操作的基本单元
@Autowired
// 客服端 : RedisTemplate 以对象作为Key 和 Value,内部对数据进行序列化 操作
private RedisTemplate redisTemplate;
@Autowired
private StringRedisTemplate stringRedisTemplate; // 以字符串 操作的基本单元
@Test
public void setRedisTemplate(){
ValueOperations ops = redisTemplate.opsForValue();
ops.set("age",42);
}
@Test
public void getRedisTemplate(){
ValueOperations ops = redisTemplate.opsForValue();
Object age = ops.get("age");
System.out.println(age); // 空值
}
@Test
public void getStringRedisTemplate(){
ValueOperations<String,String> ops = stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue();
String age = ops.get("age");
System.out.println(age);
}
}import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.TimeZone;
@Configuration
public class MyRedisConfig {
@Resource
private RedisConnectionFactory factory;
@Bean
public RedisTemplate redisTemplate(){
RedisTemplate<String,Object> redisTemplate = new RedisTemplate<>();
redisTemplate.setConnectionFactory(factory);
redisTemplate.setKeySerializer(new StringRedisSerializer());
// String 类型序列化 json
Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer<Object> serializer = new Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer<>(Object.class);
redisTemplate.setValueSerializer(serializer);
ObjectMapper om = new ObjectMapper();
om.setVisibility(PropertyAccessor.ALL, JsonAutoDetect.Visibility.ANY);
om.setDateFormat(new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss"));
om.setTimeZone(TimeZone.getDefault());
om.configure(MapperFeature.USE_ANNOTATIONS, false);
om.configure(DeserializationFeature.FAIL_ON_UNKNOWN_PROPERTIES, false);
om.configure(SerializationFeature.FAIL_ON_EMPTY_BEANS, false);
om.activateDefaultTyping(LaissezFaireSubTypeValidator.instance
,ObjectMapper.DefaultTyping.NON_FINAL, JsonTypeInfo.As.PROPERTY);
om.setSerializationInclusion(JsonInclude.Include.NON_NULL);
serializer.setObjectMapper(om);
return redisTemplate;
}
}- 客服端 : RedisTemplate 以对象作为Key 和 Value,内部对数据进行序列化 操作
3. jedis 客户端实现技术切换
<!--jedis-->
<dependency>
<groupId>redis.clients</groupId>
<artifactId>jedis</artifactId>
</dependency>spring:
redis:
host: localhost
port: 6379
client-type: jedis
lettuce:
pool:
max-active: 16
jedis:
pool:
max-active: 16lettcus 与 jedis 区别
jedis 连接 Redis 服务器是直连模式,当线程模式下使用 jedis 会存在线程安全问题,解决方案通过配置连接池使每个连接专用,这样整体性能就大受影响。
lettcus 基于 Netty 框架进行与 Redis 服务器连接,底层设计采用 StatefulRedisConnection。StatefulRedisConnection 自身是线程安全的,可以保障并发访问安全问题,所以一个连接可以被多线程复用。当然 lettcus 也支持多连接实例一起工作。
2. Mongo
1. MongoDB 特性
- MongoDB 开源,高性能,无模式的文档型数据库
2. Mysql Redis 弊端
Mysql
- 有 结构化数据, 较低的响应需求
Redis
- 无 结构化数据, 较高的响应需求
3. 数据分析
- 用户数据: 永久性存储,修改频度极低
- 游戏数据: 永久性存储和临时性存储结合,修改频度较高
- 直播数据: 永久性存储和临时性存储结合,修改频度极高
- 物联网数据: 临时性存储, 修改频率飞速
4. Mongo 运行
# 手动创建 ..\data\db 文件夹
mongod --dbpath=..\data\db
# 运行客服端 自定义参数
mongo --host=127.0.0.1 --port=27017
5. Mongo 整合
<!--MongoDB 整合-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-mongodb</artifactId>
<version>3.1.2</version>
</dependency>spring:
datasource:
mongodb:
uri: mongodb://localhost/wabisabifagpackage top.wabisabifag;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.data.mongodb.core.MongoTemplate;
import java.awt.print.Book;
@SpringBootTest
public class Application {
@Autowired
private MongoTemplate mongoTemplate;
@Test
public void setMongoTemplate(){
Book book = new Book(1,"spring","spring","spring");
mongoTemplate.save(book);
}
@Test
public void find(){
List<Book> all = mongoTemplate.findAll(Book.class);
System.out.println(all);
}
}3. ES
Elasticsearch 是一个分布式全文搜索引擎
端口号: 9200
1. 索引操作
- 幂等性,指的是相同参数下,一次请求和多次请求的结果是相等的
- get,put,delete请求都是幂等的
2. 文档操作
以下内容在 postman 中执行
- 数据生成
- post 生成指定id http://localhost:9200/bools/_create
- post 生成随机id http://localhost:9200/bools/_doc
- post 生成指定id http://localhost:9200/bools/_doc/1
- body {“id”:1,”name”:”spring”,”type”:”spring”,”description”:”spring”}
- 数据 id 查询
- get 查询指定id http://localhost:9200/bools/_doc/1
- get 查询所有id http://localhost:9200/bools/_search
- 数据 条件 查询
- 数据 id 删除
- delete 删除指定id http://localhost:9200/bools/_doc/1
- 数据 id 修改
- put 修改指定id 全部数据 http://localhost:9200/bools/_doc/1
- post 修改指定id 指定数据 http://localhost:9200/bools/_update/1
- body {“doc”:{“name”:”springboot”} }
3. Elasticsearch 整合
- Low level
<!--elasticsearch 整合-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-elasticsearch</artifactId>
</dependency>spring:
datasource:
druid:
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/smbms
username: root
password: 123456
driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
elasticsearch:
rest:
uris: http://localhost:9200
mybatis-plus:
configuration:
# 日志
log-impl: org.apache.ibatis.logging.stdout.StdOutImpl
global-config:
db-config:
table-prefix: smbms_
id-type: autopackage top.wabisabifag;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.data.elasticsearch.core.ElasticsearchRestTemplate;
import java.awt.print.Book;
import java.util.List;
@SpringBootTest
public class Application {
@Autowired
private ElasticsearchRestTemplate template;
@Test
public void fn(){
template.get(new Book(1,"a","a","a"));
}
}- Hight level (方法过时,已经有新的整合内容 ===》》 application.yml 配置参数)
<!--elasticsearch 整合-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.elasticsearch.client</groupId>
<artifactId>elasticsearch-rest-high-level-client</artifactId>
</dependency>package top.wabisabifag;
import org.apache.http.HttpHost;
import org.elasticsearch.client.RequestOptions;
import org.elasticsearch.client.RestClient;
import org.elasticsearch.client.RestClientBuilder;
import org.elasticsearch.client.RestHighLevelClient;
import org.elasticsearch.client.indices.CreateIndexRequest;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.AfterEach;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.BeforeEach;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.data.elasticsearch.core.ElasticsearchRestTemplate;
import java.awt.print.Book;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.List;
@SpringBootTest
public class Application {
@Autowired
private RestHighLevelClient client;
@BeforeEach
void setUp(){
this.client = new RestHighLevelClient(RestClient.builder(HttpHost.create("http://localhost:9200")));
}
@AfterEach
void tearDown() throws IOException{
this.client.close();
}
@Test
public void testCreateClient(){
<!-- // 创建客服端
HttpHost host = HttpHost.create("http://localhost:9200");
RestClientBuilder builder = RestClient.builder(host);
client = new RestHighLevelClient(builder);
// 发送请求 名叫books的索引
CreateIndexRequest request = new CreateIndexRequest("books");
client.indices().create(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
client.close(); -->
CreateIndexRequest request = new CreateIndexRequest("books");
client.indices().create(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
}
}
4. 分词器 和 创建索引属性
<!--String 转换为 json-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>fastjson</artifactId>
<version>1.2.78</version>
</dependency>@SpringBootTest
public class Application {
/* 创建索引*/
@Test
public void testCreateIndex() throws IOException{
CreateIndexRequest request = new CreateIndexRequest("books");
client.indices().create(request,RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
}
/* 创建索引 By IK*/
@Test
public void testCreateIndexByIK() throws IOException{
CreateIndexRequest request = new CreateIndexRequest("books");
String json = "";
// 设置请求中的参数
request.source(json, XContentType.JSON);
client.indices().create(request,RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
}
/* 添加文档 */
@Test
public void testCreateDoc() throws IOException{
/* 1.查询单个id */
Book book = bookDao.selectByID(1);
IndexRequest request = new IndexRequest("books").id(book.getId().toString());
/* fastjson 依赖: 对象转化为 json*/
String json = JSON.toJSONString(book);
request.source(json,XContentType.JSON);
client.index(request,RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
/* 2. 查询所有id*/
List<Book> bookList = bookDao.selectList(null);
/* 批处理请求 */
BulkRequest request = new BulkRequest();
for (Book book : bookList) {
IndexRequest request = new IndexRequest("books").id(book.getId().toString());
String json = JSON.toJSONString(book);
request.source(json,XContentType.JSON);
request.add(request);
}
client.bulk(request,RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
}
}8. 整合第三方技术
1. 缓存 (部分过时,以最新为主,自行理解)
- 一种介质于数据永久存储介质可数据应用之间的数据临时存储介质
- 缓存可减少低速数据速过程的次数,提高系统性能。如:磁盘IO,
- 提高永久性存储介质的数据读取效率,提供临时数据存储空间
- SpringBoot 提供其他缓存技术整合,统一接口,方便缓存技术开发管理
- Generic
- JCache
- Ehcache
- Hazelcast
- infinispan
- Couchbase
- Redis
- Caffenine
- Simple (内存级 默认)
- memcached
- jetcache (阿里)
- j2cache
1. 模拟缓存
package top.wabisabifag.service.impl;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import top.wabisabifag.dao.BookDao;
import top.wabisabifag.domain.Book;
import java.util.HashMap;
@Service
public class BookServiceImpl {
@Autowired
private BookDao bookDao;
/* 对应缓存 */
private HashMap<Integer,Book> cache = new HashMap<Integer, Book>();
public Book getById(Integer id){
/* 缓存中没有本次查询数据,访问数据库*/
Book book = cache.get(id);
if(book == null){
Book queryBook = bookDao.selectById(id);
cache.put(id,queryBook);
return queryBook;
}
return cache.get(id);
}
public boolean save(Book book){
return bookDao.insert(book) > 0;
}
}2. 模拟验证
package top.wabisabifag.service.impl;
import top.wabisabifag.service.MsgService;
import java.util.HashMap;
public class MsgServiceImpl implements MsgService {
private HashMap<String,String> cache = new HashMap<String,String>();
@Override
public String get(String tele) {
/* 获取后6位数据*/
String code = tele.substring(tele.length() - 6);
cache.put(tele,code);
return code;
}
@Override
public boolean check(String tele, String code) {
String queryCode = cache.get(tele);
return code.equals(queryCode);
}
}package top.wabisabifag.config;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
import top.wabisabifag.service.MsgService;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/msg")
public class MsgControll {
@Autowired
private MsgService msgService;
@GetMapping("{tele}")
public String get(@PathVariable String tele){
return msgService.get(tele);
}
@GetMapping
public boolean check(String tele,String code){
return msgService.check(tele, code);
}
}3. SpringBoot 缓存
<!--SpringBoot 缓存-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-cache</artifactId>
<version>1.2.78</version>
</dependency>
<!--Nosql整合数据库-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
</dependency>package top.wabisabifag;
import org.mybatis.spring.annotation.MapperScan;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.EnableCaching;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
@SpringBootApplication
@MapperScan("top.wabisabifag.dao") /*使用@MapperScan可以指定要扫描的Mapper类的包的路径*/
@ComponentScan(basePackages={"top.wabisabifag"})
@EnableCaching /* 开启缓存*/
public class application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 线程安全问题
SpringApplication.run(application.class,args);
// 不接受外部临时参数
SpringApplication.run(application.class);
}
}package top.wabisabifag.service.impl;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.Cacheable;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import top.wabisabifag.dao.BookDao;
import top.wabisabifag.domain.Book;
import java.util.HashMap;
@Service
public class BookServiceImpl {
@Autowired
private BookDao bookDao;
@Override
@Cacheable(value = "cacheSpace",key = "#id")
public Book getById(Integer id){
return bookDao.selectById(id);
}
}4. 模拟短信验证(Simple)
package top.wabisabifag.domain;
import lombok.Data;
@Data
public class SMSCode {
private String tele;
private String Code;
}package top.wabisabifag.service;
import top.wabisabifag.domain.SMSCode;
public interface SMSCodeService {
public String sendCodeToSMS(String tele);
public boolean checkCode(SMSCode smsCode);
}package top.wabisabifag.service.impl;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.CachePut;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.Cacheable;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import top.wabisabifag.domain.SMSCode;
import top.wabisabifag.service.SMSCodeService;
import top.wabisabifag.utils.CodeUtils;
@Service
public class SMSCodeServiceImpl implements SMSCodeService {
@Autowired
private CodeUtils codeUtils;
@Override
/*@Cacheable(value = "smsCode",key = "#tele") // 可以存放和读取,不适用于验证码重新获取*/
@CachePut(value = "smsCode",key = "#tele")
public String sendCodeToSMS(String tele) {
String code = codeUtils.generator(tele);
return code;
}
@Override
public boolean checkCode(SMSCode smsCode) {
String code = smsCode.getCode();
String cacheCode = codeUtils.get(smsCode.getTele());
return code.equals(cacheCode);
}
}package top.wabisabifag.config;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import top.wabisabifag.domain.SMSCode;
import top.wabisabifag.service.SMSCodeService;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/sms")
public class SMSCodeController {
@Autowired
private SMSCodeService service;
@GetMapping
public String getCode(String tele){
String code = service.sendCodeToSMS(tele);
return code;
}
@PostMapping
public boolean checkCode(SMSCode smsCode){
return service.checkCode(smsCode);
}
}package top.wabisabifag.utils;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.Cacheable;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component /* 设置为bean,对方注解调用*/
public class CodeUtils {
private String[] patch={"00000","0000","000","00","0",""};
public String generator(String tele){
/* 加密码 */
int encryption = 20230929;
int hash = tele.hashCode();
long nowTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
long result = hash ^ encryption;
result = result ^ nowTime;
/*
* 问题
* 1. 负数问题
* 2. 前置位为 0 。如: 001233,输出: 1233问题
*/
long code = result % 1000000;
/* 防止负数*/
code = code<0 ? -code:code;
/* 补零 */
String codeString = code + "";
int len = codeString.length();
return patch[len-1]+codeString;
}
/* 该方法不放置于 ServiceImpl,就算有注解也被认为普通方法
* bean方法不能自我调用
*/
@Cacheable(value = "smsCode",key = "#tele")
public String get(String tele){
return null;
}
/* *//* 功能验证*//*
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(new CodeUtils().generator("18866668888") );;
}*/
}5. Ehcache Redis memcached 缓存统一接口配置
1. Ehcache Redis
<!--Ehcache 缓存-->
<dependency>
<groupId>net.sf.ehcache</groupId>
<artifactId>ehcache</artifactId>
</dependency>// 统一接口
spring:
# 配置缓存类型
cache:
# ehcache (文档配置)
#type: ehcache
#ehcache: ehcache.xml
# redis (yml配置)
type: redis
redis:
host: localhost
port: 6379
use-key-prefix: true # 是否使用前缀
cache-null-values: false # 是否缓存空值
key-prefix: sms_ # 指定前缀
time-to-live: # 活动时间
datasource:
druid:
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/smbms
username: root
password: 123456
driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
elasticsearch:
rest:
uris: http://localhost:9200<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<ehcache xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:noNamespaceSchemaLocation="http://ehcache.org/ehcache.xsd"
updateCheck="false" name="defaultCache">
<!--
diskStore:为缓存路径,ehcache分为内存和磁盘两级,此属性定义磁盘的缓存位置,可以自定义目录,确保用户有权限即可。参数解释如下:
user.home – 用户主目录
user.dir – 用户当前工作目录
java.io.tmpdir – 默认临时文件路径
-->
<!-- <diskStore path="java.io.tmpdir"/> -->
<diskStore path="C:/Users/admin/ehcache/"/>
<!-- maxElementsInMemory:内存中最大缓存对象数,根据服务器资源配置 -->
<!-- eternal: 默认为false,设置true表示对象永不过期,此时会忽略timeToIdleSeconds和timeToLiveSeconds属性, -->
<!-- maxElementsOnDisk:硬盘中最大缓存对象数,若是0表示无穷大 -->
<!-- overflowToDisk:true表示当内存缓存的对象数目达到了maxElementsInMemory界限后,会把溢出的对象写到硬盘缓存中。
注意:如果缓存的对象要写入到硬盘中的话,则该对象必须实现了Serializable接口才行。-->
<!-- diskSpoolBufferSizeMB:磁盘缓存区大小,默认为30MB。每个Cache都应该有自己的一个缓存区。-->
<!-- diskPersistent:是否缓存虚拟机重启期数据 -->
<!-- diskExpiryThreadIntervalSeconds:磁盘失效线程运行时间间隔,默认为120秒 -->
<!-- timeToIdleSeconds: 设定允许对象处于空闲状态的最长时间,单位(秒)。自对象最近一次被访问后,
空闲时间超过了timeToIdleSeconds属性值,这个对象就会过期,如果该属性值为0,则对象无限期地处于空闲状态
EHCache将把它从缓存中清空。只有当eternal属性为false,该属性才有效。
-->
<!-- timeToLiveSeconds:设定允许对象存在于缓存中的最长时间,单位(秒)。自对象被存放到缓存中后,
在缓存中的时间超过了timeToLiveSeconds属性值,这个对象就会过期,如果该属性值为0,则对象无限期地存在于缓存中。
EHCache将把它从缓存中清除。只有当eternal属性为false,该属性才有效。timeToLiveSeconds必须大于timeToIdleSeconds属性,才有意义 -->
<!-- memoryStoreEvictionPolicy:当达到maxElementsInMemory限制时,Ehcache将会根据指定的策略去清理内存。
可选策略有:LRU(最近最少使用,默认策略)、FIFO(先进先出)、LFU(最少访问次数)。-->
<!-- 默认缓存 -->
<defaultCache
maxElementsInMemory="10000"
eternal="false"
overflowToDisk="false"
diskSpoolBufferSizeMB="50"
timeToIdleSeconds="300"
timeToLiveSeconds="600"
maxElementsOnDisk="10000000"
diskExpiryThreadIntervalSeconds="120"
memoryStoreEvictionPolicy="LRU">
<persistence strategy="localTempSwap"/>
</defaultCache>
<cache name="employee_all"
maxElementsInMemory="100"
eternal="false"
overflowToDisk="true"
timeToIdleSeconds="300"
timeToLiveSeconds="600"
memoryStoreEvictionPolicy="LRU"/>
<cache name="employee_info"
maxElementsInMemory="1000"
eternal="false"
overflowToDisk="true"
timeToIdleSeconds="300"
timeToLiveSeconds="600"
memoryStoreEvictionPolicy="LRU"/>
<!--设置缓存空间-->
<cache name="smsCode"
maxElementsInMemory="1000"
eternal="false"
overflowToDisk="true"
timeToIdleSeconds="60"
timeToLiveSeconds="60"
memoryStoreEvictionPolicy="LRU"/>
</ehcache>2. memcached 缓存整合
- memcached 特性
- memcached Client for Java: 最早期客服端,稳定,用户群广
- SpyMemcached: 效率高
- Xmemcached: 并发处理好
- 暂未被SpringBoot 整合,硬编码方式实现客服端初始化管理
- memcached 安装
- memcached
- 管理员权限 操作命令行:
- 安装: memcached.exe -d install
- 启动: emcached.exe -d start
- 关闭: emcached.exe -d stop
<!--memcached 缓存-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.googlecode</groupId>
<artifactId>xmemcached</artifactId>
<version>2.4.7</version>
</dependency>ppackage top.wabisabifag.config;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import java.io.IOException;
public class XMemcachedConfig {
@Bean
public MemcachedClient getMemcachedClient() throws IOException {
MemcachedClientBuilder memcachedClientBuilder = new XMemcachedClientBuilder("localhost:11211");
MemcachedClient memcachedClient = memcachedClientBuilder.build();
return memcachedClient;
}
}
>>>>>>>>>>优>>>>>化>>>>>配>>>>>>置>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>
package top.wabisabifag.config;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import java.io.IOException;
@Configuration
public class XMemcachedConfig {
@Autowired
private XMemcachedProperties memcachedProperties;
@Bean
public MemcachedClient getMemcachedClient() throws IOException {
MemcachedClientBuilder memcachedClientBuilder = new XMemcachedClientBuilder(memcachedProperties.getServers());
memcachedProperties.setPoolSize(memcachedProperties.getPoolSize());
memcachedProperties.setOpTimeout(memcachedProperties.getOpTimeout());
MemcachedClient memcachedClient = memcachedClientBuilder.build();
return memcachedClient;
}
}package top.wabisabifag.service.impl;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.CachePut;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.Cacheable;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import top.wabisabifag.domain.SMSCode;
import top.wabisabifag.service.SMSCodeService;
import top.wabisabifag.utils.CodeUtils;
@Service
public class SMSCodeServiceImpl implements SMSCodeService {
@Autowired
private MemcachedClient memcachedClient;
@Override
public String sendCodeToSMS(String tele) {
String code = codeUtils.generator(tele);
// key 有效时间 值
memcachedClient.set(tele,0,code);
return code;
}
@Override
public boolean checkCode(SMSCode smsCode) {
String code = memcachedClient.get(smsCode.getTele()).toString();
return smsCode.getCode().equals(code);
}
}spring:
# 配置缓存类型
cache:
# memcached
servers: localhost:11211
poolSize: 10
opTimeout: 3000package top.wabisabifag.config;
import lombok.Data;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "memcached")
@Data
public class XMemcachedProperties {
private String servers;
private int poolSize;
private long opTimeout;
}6. jetCache
1. jetCache 特性
- jetCache 对 SpringCache 进行封装,原有基础上实现多级缓存,缓存统计,自动刷新,异步调用,数据报表等功能。
- jetCache 设定本地缓存 和 远程缓存 的多级缓存解决方案
- 本地缓存
- LinkedHashMap
- Caffeine
- 远程缓存
- Redis
- Tair
- 本地缓存
2. 整体部署(基础)
<!--jetCache 阿里缓存整合方案-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alicp.jetcache</groupId>
<artifactId>jetcache-starter-redis</artifactId>
<version>2.4.7</version>
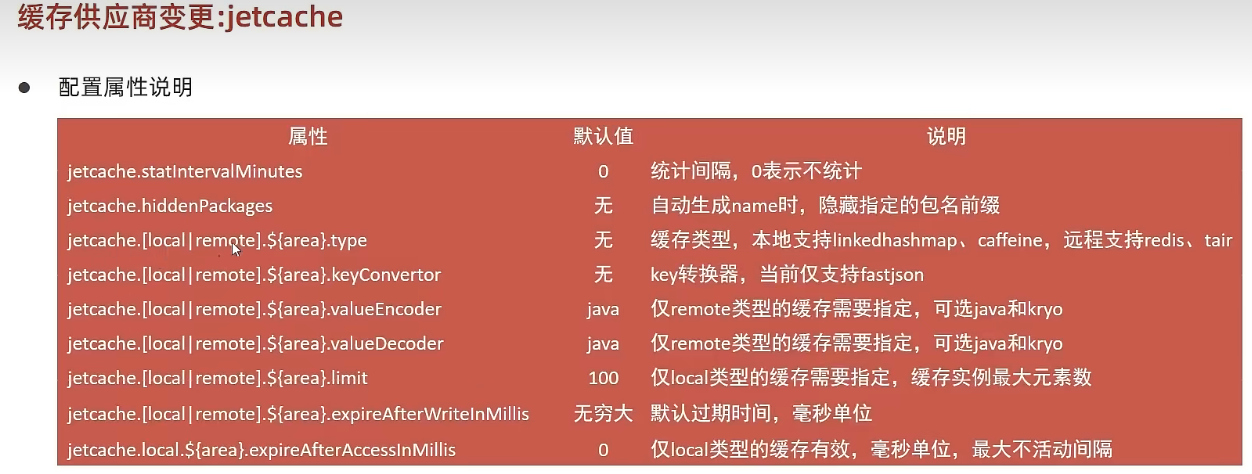
</dependency> # jetcache 阿里缓存配置
jetcache:
# 每过 一段时间 在控制台上显示一段数据
statIntervalMinutes: 15
# 远程访问的 area 的名称 是否进入 缓存名中
areaInCacheName: false
# 本地
local:
default:
type: linkedhashmap
# 为方便对象转换为字符粗串:key必须为字符串
keyConvertor: fastjson
# 缓存的数据量
limit: 100
# 远程
remote:
default:
type: redis
host: localhost
port: 6379
# 为方便对象转换为字符粗串:key必须为字符串
# jetCache 的方法缓存 注解方式时需要
keyConvertor: fastjson
valueEncoder: java
valueDecoder: java
# 初始化连接池
poolConfig:
minIdle: 5
maxIdle: 20
maxTotal: 50
sms:
type: redis
host: localhost
port: 6379
poolConfig:
maxTotal: 50package top.wabisabifag;
import org.mybatis.spring.annotation.MapperScan;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.EnableCaching;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
@SpringBootApplication
/* jetCache 开关: 启用注解方式开启缓存*/
@EnableCreateCacheAnnotation
public class application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 线程安全问题
SpringApplication.run(application.class,args);
// 不接受外部临时参数
SpringApplication.run(application.class);
}
}package top.wabisabifag.service.impl;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.CachePut;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.Cacheable;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import top.wabisabifag.domain.SMSCode;
import top.wabisabifag.service.SMSCodeService;
import top.wabisabifag.utils.CodeUtils;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
@Service
public class SMSCodeServiceImpl implements SMSCodeService {
@Autowired
private CodeUtils codeUtils;
# 通过 area="sms" 调用远程缓存的自定义前缀
@CreateCache(area="sms",name="jetCache",expire=3600,timeUnit= TimeUnit.SECONDS)
private Cache<String,String> jetCache;
@Override
public String sendCodeToSMS(String tele) {
String code = codeUtils.generator(tele);
jetCache.put(tele,code);
return code;
}
@Override
public boolean checkCode(SMSCode smsCode) {
String code = jetCache.get(smsCode.getTele());
return smsCode.getCode().equals(code);
}
}package top.wabisabifag.service.impl;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.CachePut;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.Cacheable;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import top.wabisabifag.domain.SMSCode;
import top.wabisabifag.service.SMSCodeService;
import top.wabisabifag.utils.CodeUtils;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
@Service
public class SMSCodeServiceImpl implements SMSCodeService {
@Autowired
private CodeUtils codeUtils;
# 设定缓存类型: 仅用 本地缓存
@CreateCache(name="jetCache",expire=3600,timeUnit= TimeUnit.SECONDS,cacheType= CacheType.LOCAL)
private Cache<String,String> jetCache;
@Override
public String sendCodeToSMS(String tele) {
String code = codeUtils.generator(tele);
jetCache.put(tele,code);
return code;
}
@Override
public boolean checkCode(SMSCode smsCode) {
String code = jetCache.get(smsCode.getTele());
return smsCode.getCode().equals(code);
}
}3. jetCache 方法缓存(改动基础)
package top.wabisabifag;
import org.mybatis.spring.annotation.MapperScan;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.EnableCaching;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
@SpringBootApplication
/* jetCache 开关: 启用注解方式开启缓存*/
@EnableCreateCacheAnnotation
/* 开启注解缓存: 包名覆盖 */
@EnableMethodCache(basePackages = "top.wabisabifag")
public class application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 线程安全问题
SpringApplication.run(application.class,args);
// 不接受外部临时参数
SpringApplication.run(application.class);
}
}package top.wabisabifag.domain;
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Data;
import java.io.Serializable;
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
/* jetCache 缓存 Java 的对象时
映入 Redis 库不支持。( 序列化和反序列化问题*/
public class Book implements Serializable {
private int id;
private String name;
private String type;
private String description;
}package top.wabisabifag.service.impl;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.Cacheable;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import top.wabisabifag.dao.BookDao;
import top.wabisabifag.domain.Book;
import java.util.HashMap;
@Service
public class BookServiceImpl {
@Autowired
private BookDao bookDao;
/* 对应缓存 */
private HashMap<Integer,Book> cache = new HashMap<Integer, Book>();
@Override
//@Cacheable(value = "cacheSpace",key = "#id")
@Cached(name="book",key="#id",expire=3600)
public Book getById(Integer id){
return bookDao.selectById(id);
}
}
package top.wabisabifag.service.impl;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.Cacheable;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import top.wabisabifag.dao.BookDao;
import top.wabisabifag.domain.Book;
import java.util.HashMap;
@Service
public class BookServiceImpl {
@Autowired
private BookDao bookDao;
/* 对应缓存 */
private HashMap<Integer,Book> cache = new HashMap<Integer, Book>();
@Override
/* 注入缓存注解*/
@Cached(name="book",key="#id",expire=3600)
/* 刷新: 内存和数据库内容不同步*/
@CacheRefresh(refresh=10)
public Book getById(Integer id){
return bookDao.selectById(id);
}
@Override
/* 更新缓存注解*/
@CacheUpdate(name="book_",key="#book.id",value="#book")
public boolean update(Book book){
return bookDao.updateById(book)>0;
}
@Override
/* 删除缓存注解*/
@CacheInvalidate(name="book_",key="#id",value="#book")
public boolean update(Book book){
return bookDao.updateById(book)>0;
}
}7. j2cache
1. j2cache 特性
- j2cache 是一个缓存整合框架,可提供缓存的整合方案,使用各种缓存搭配使用。(自身不提供缓存功能
2. j2cache (主要整合 Redis Ehcache)
<!--j2Cache 核心-->
<dependency>
<groupId>net-oschina.j2cache</groupId>
<artifactId>j2cache-core</artifactId>
<version>2.8.4-release</version>
</dependency>
<!--jetCache SpringBoot整合-->
<dependency>
<groupId>net-oschina.j2cache</groupId>
<artifactId>j2cache-spring-boot2-starter</artifactId>
<version>2.8.0-release</version>
</dependency>
<!--Ehcache 缓存-->
<dependency>
<groupId>net.sf.ehcache</groupId>
<artifactId>ehcache</artifactId>
</dependency> # j2cache 整合
j2cache:
# j2cache 配置文件名
config-location: j2cache.properties# 1级缓存
j2cache.L1.provider_class= ehcache
ehcache.configXml = ehcache.xml
# 是否开启二级缓存
j2cache.l2-cache-open = ture
# 1级缓存中的数据如何到达2级缓存:
# 广播方式,可以使用redis 提供的消息订阅模式,也可以使用jgroups多播实现
j2cache.broadcast = net.oschina.j2cache.cache.support.redis.SpringRedisPubSubPolicy
# 2级缓存
j2cache.L2.provider_class = net.oschina.j2cache.cache.support.redis.SpringRedisProvider
j2cache.L2.config_section = redis
redis.hosts = localhost:6379
redis.mode = single
redis.namespace =j2cache
##J2Cache configuration
##########################################
## Cache Broadcast Method
## values:
## jgroups -> use jgroups's multicast
## redis -> use redis publish/subscribe mechanism (using jedis)
## lettuce -> use redis publish/subscribe mechanism (using lettuce, Recommend)
## rabbitmq -> use RabbitMQ publisher/consumer mechanism
## rocketmq -> use RocketMQ publisher/consumer mechanism
## none -> don't notify the other nodes in cluster
## xx.xxxx.xxxx.Xxxxx your own cache broadcast policy classname that implement net.oschina.j2cache.cluster.ClusterPolicy
##########################################
#j2cache.broadcast = redis
#
## jgroups properties
#jgroups.channel.name = j2cache
#jgroups.configXml = /network.xml
#
## RabbitMQ properties
#rabbitmq.exchange = j2cache
#rabbitmq.host = localhost
#rabbitmq.port = 5672
#rabbitmq.username = guest
#rabbitmq.password = guest
#
## RocketMQ properties
#rocketmq.name = j2cache
#rocketmq.topic = j2cache
## use ; to split multi hosts
#rocketmq.hosts = 127.0.0.1:9876
#
##########################################
## Level 1&2 provider
## values:
## none -> disable this level cache
## ehcache -> use ehcache2 as level 1 cache
## ehcache3 -> use ehcache3 as level 1 cache
## caffeine -> use caffeine as level 1 cache(only in memory)
## redis -> use redis as level 2 cache (using jedis)
## lettuce -> use redis as level 2 cache (using lettuce)
## readonly-redis -> use redis as level 2 cache ,but never write data to it. if use this provider, you must uncomment `j2cache.L2.config_section` to make the redis configurations available.
## memcached -> use memcached as level 2 cache (xmemcached),
## [classname] -> use custom provider
##########################################
#
#j2cache.L1.provider_class = caffeine
#j2cache.L2.provider_class = redis
#
## When L2 provider isn't `redis`, using `L2.config_section = redis` to read redis configurations
## j2cache.L2.config_section = redis
#
## Enable/Disable ttl in redis cache data (if disabled, the object in redis will never expire, default:true)
## NOTICE: redis hash mode (redis.storage = hash) do not support this feature)
#j2cache.sync_ttl_to_redis = true
#
## Whether to cache null objects by default (default false)
#j2cache.default_cache_null_object = true
#
##########################################
## Cache Serialization Provider
## values:
## fst -> using fast-serialization (recommend)
## kryo -> using kryo serialization
## json -> using fst's json serialization (testing)
## fastjson -> using fastjson serialization (embed non-static class not support)
## java -> java standard
## fse -> using fse serialization
## [classname implements Serializer]
##########################################
#
#j2cache.serialization = json
##json.map.person = net.oschina.j2cache.demo.Person
#
##########################################
## Ehcache configuration
##########################################
#
## ehcache.configXml = /ehcache.xml
#
## ehcache3.configXml = /ehcache3.xml
## ehcache3.defaultHeapSize = 1000
#
##########################################
## Caffeine configuration
## caffeine.region.[name] = size, xxxx[s|m|h|d]
##
##########################################
#caffeine.properties = /caffeine.properties
#
##########################################
## Redis connection configuration
##########################################
#
##########################################
## Redis Cluster Mode
##
## single -> single redis server
## sentinel -> master-slaves servers
## cluster -> cluster servers (数据库配置无效,使用 database = 0)
## sharded -> sharded servers (密码、数据库必须在 hosts 中指定,且连接池配置无效); redis://user:password@127.0.0.1:6379/0)
##
##########################################
#
#redis.mode = single
#
##redis storage mode (generic|hash)
#redis.storage = generic
#
### redis pub/sub channel name
#redis.channel = j2cache
### redis pub/sub server (using redis.hosts when empty)
#redis.channel.host =
#
##cluster name just for sharded
#redis.cluster_name = j2cache
#
### redis cache namespace optional, default[empty]
#redis.namespace =
#
### redis command scan parameter count, default[1000]
##redis.scanCount = 1000
#
### connection
## Separate multiple redis nodes with commas, such as 192.168.0.10:6379,192.168.0.11:6379,192.168.0.12:6379
#
#redis.hosts = 127.0.0.1:6379
#redis.timeout = 2000
#redis.password =
#redis.database = 0
#redis.ssl = false
#
### redis pool properties
#redis.maxTotal = 100
#redis.maxIdle = 10
#redis.maxWaitMillis = 5000
#redis.minEvictableIdleTimeMillis = 60000
#redis.minIdle = 1
#redis.numTestsPerEvictionRun = 10
#redis.lifo = false
#redis.softMinEvictableIdleTimeMillis = 10
#redis.testOnBorrow = true
#redis.testOnReturn = false
#redis.testWhileIdle = true
#redis.timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis = 300000
#redis.blockWhenExhausted = false
#redis.jmxEnabled = false
#
##########################################
## Lettuce scheme
##
## redis -> single redis server
## rediss -> single redis server with ssl
## redis-sentinel -> redis sentinel
## redis-cluster -> cluster servers
##
##########################################
#
##########################################
## Lettuce Mode
##
## single -> single redis server
## sentinel -> master-slaves servers
## cluster -> cluster servers (数据库配置无效,使用 database = 0)
## sharded -> sharded servers (密码、数据库必须在 hosts 中指定,且连接池配置无效 ; redis://user:password@127.0.0.1:6379/0)
##
##########################################
#
### redis command scan parameter count, default[1000]
##lettuce.scanCount = 1000
#lettuce.mode = single
#lettuce.namespace =
#lettuce.storage = hash
#lettuce.channel = j2cache
#lettuce.scheme = redis
#lettuce.hosts = 127.0.0.1:6379
#lettuce.password =
#lettuce.database = 0
#lettuce.sentinelMasterId =
#lettuce.maxTotal = 100
#lettuce.maxIdle = 10
#lettuce.minIdle = 10
## timeout in milliseconds
#lettuce.timeout = 10000
## redis cluster topology refresh interval in milliseconds
#lettuce.clusterTopologyRefresh = 3000
#
##########################################
## memcached server configurations
## refer to https://gitee.com/mirrors/XMemcached
##########################################
#
#memcached.servers = 127.0.0.1:11211
#memcached.username =
#memcached.password =
#memcached.connectionPoolSize = 10
#memcached.connectTimeout = 1000
#memcached.failureMode = false
#memcached.healSessionInterval = 1000
#memcached.maxQueuedNoReplyOperations = 100
#memcached.opTimeout = 100
#memcached.sanitizeKeys = false<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<ehcache xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:noNamespaceSchemaLocation="http://ehcache.org/ehcache.xsd"
updateCheck="false" name="defaultCache">
<!--
diskStore:为缓存路径,ehcache分为内存和磁盘两级,此属性定义磁盘的缓存位置,可以自定义目录,确保用户有权限即可。参数解释如下:
user.home – 用户主目录
user.dir – 用户当前工作目录
java.io.tmpdir – 默认临时文件路径
-->
<!-- <diskStore path="java.io.tmpdir"/> -->
<diskStore path="C:/Users/admin/ehcache/"/>
<!-- maxElementsInMemory:内存中最大缓存对象数,根据服务器资源配置 -->
<!-- eternal: 默认为false,设置true表示对象永不过期,此时会忽略timeToIdleSeconds和timeToLiveSeconds属性, -->
<!-- maxElementsOnDisk:硬盘中最大缓存对象数,若是0表示无穷大 -->
<!-- overflowToDisk:true表示当内存缓存的对象数目达到了maxElementsInMemory界限后,会把溢出的对象写到硬盘缓存中。
注意:如果缓存的对象要写入到硬盘中的话,则该对象必须实现了Serializable接口才行。-->
<!-- diskSpoolBufferSizeMB:磁盘缓存区大小,默认为30MB。每个Cache都应该有自己的一个缓存区。-->
<!-- diskPersistent:是否缓存虚拟机重启期数据 -->
<!-- diskExpiryThreadIntervalSeconds:磁盘失效线程运行时间间隔,默认为120秒 -->
<!-- timeToIdleSeconds: 设定允许对象处于空闲状态的最长时间,单位(秒)。自对象最近一次被访问后,
空闲时间超过了timeToIdleSeconds属性值,这个对象就会过期,如果该属性值为0,则对象无限期地处于空闲状态
EHCache将把它从缓存中清空。只有当eternal属性为false,该属性才有效。
-->
<!-- timeToLiveSeconds:设定允许对象存在于缓存中的最长时间,单位(秒)。自对象被存放到缓存中后,
在缓存中的时间超过了timeToLiveSeconds属性值,这个对象就会过期,如果该属性值为0,则对象无限期地存在于缓存中。
EHCache将把它从缓存中清除。只有当eternal属性为false,该属性才有效。timeToLiveSeconds必须大于timeToIdleSeconds属性,才有意义 -->
<!-- memoryStoreEvictionPolicy:当达到maxElementsInMemory限制时,Ehcache将会根据指定的策略去清理内存。
可选策略有:LRU(最近最少使用,默认策略)、FIFO(先进先出)、LFU(最少访问次数)。-->
<!-- 默认缓存 -->
<defaultCache
maxElementsInMemory="10000"
eternal="false"
overflowToDisk="false"
diskSpoolBufferSizeMB="50"
timeToIdleSeconds="300"
timeToLiveSeconds="600"
maxElementsOnDisk="10000000"
diskExpiryThreadIntervalSeconds="120"
memoryStoreEvictionPolicy="LRU">
<persistence strategy="localTempSwap"/>
</defaultCache>
<cache name="employee_all"
maxElementsInMemory="100"
eternal="false"
overflowToDisk="true"
timeToIdleSeconds="300"
timeToLiveSeconds="600"
memoryStoreEvictionPolicy="LRU"/>
<cache name="employee_info"
maxElementsInMemory="1000"
eternal="false"
overflowToDisk="true"
timeToIdleSeconds="300"
timeToLiveSeconds="600"
memoryStoreEvictionPolicy="LRU"/>
<!--设置缓存空间-->
<cache name="smsCode"
maxElementsInMemory="1000"
eternal="false"
overflowToDisk="true"
timeToIdleSeconds="300"
timeToLiveSeconds="600"
memoryStoreEvictionPolicy="LRU"/>
</ehcache>package top.wabisabifag.service.impl;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.CacheType;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.CachePut;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.Cacheable;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import top.wabisabifag.domain.SMSCode;
import top.wabisabifag.service.SMSCodeService;
import top.wabisabifag.utils.CodeUtils;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
@Service
public class SMSCodeServiceImpl implements SMSCodeService {
@Autowired
private CodeUtils codeUtils;
@Autowired
/* 定义缓存对象*/
private CacheChannel cacheChannel;
@Override
public String sendCodeToSMS(String tele) {
String code = codeUtils.generator(tele);
/* 放入内缓存对象中*/
cacheChannel.set("sms",tele,code);
return code;
}
@Override
public boolean checkCode(SMSCode smsCode) {
/* 获取内缓存对象数据*/
String code = cacheChannel.get("sms",smsCode.getTele()).asString();
return smsCode.getCode().equals(code);
}
}2. 任务
定时任务
- 年度报表
- 缓存统计报告
定时任务框架技术
- Quartz
- Spring Task
package top.wabisabifag;
import java.util.Timer;
import java.util.TimerTask;
public class TimeTaskApp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/* 创建定时器对象*/
Timer timer = new Timer();
/* 创建定时任务*/
TimerTask task = new TimerTask() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("timer task run...");
}
};
/* 每过 2秒 执行定时任务*/
timer.schedule(task,0,2000);
}
}1. SpringBoot 整合 Quartz
1. 概念
- 工作(Job): 用于定义具体的工作
- 工作明细(JobDetail): 用于描述定时工作相关的信息
- 触发器(Trugger): 用于描述触发工作的规则,通常使用cron 表达式定义调度规则
- 调度器(Scheduler): 描述工作明细与触发器的对应关系
2. Quartz
<!--Quartz 整合-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-quartz</artifactId>
<scop>test</scop>
</dependency>package top.wabisabifag.quartz;
import org.springframework.scheduling.quartz.QuartzJobBean;
public class MyQuartz extends QuartzJobBean {
@Override
protected void executeInternal(JobExecutionContext jobExecutionContext) throws JobExecutionException {
}
}package top.wabisabifag.config;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import top.wabisabifag.quartz.MyQuartz;
@Configuration
public class QuartzConfig {
@Bean
/* 描述*/
public JobDetail printJobDetail(){
/* 绑定具体的工作 */
return JobBuilder.newJob(MyQuartz.class)
.storeDurably().build; //持久化对象
}
@Bean
public Trigger printJobTrigger(){
/* 设定任务执行的周期: 分 时 日 月 */
ScheduleBuilder scheduleBuilder = CronScheduleBuilder.cronSchedule("0 * * * * ?");
/* 绑定对应的工作明细*/
return TriggerBuilder
.newTrigger().forJob(printJobTrigger()) // 新建触发器 绑定任务
.withSchedule(schedBuilder).build();// 构建执行周期 绑定任务执行周期
}
}2. Spring Task
@SpringBootApplication
/* 开启定时任务功能*/
@EnableScheduling
public class application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 线程安全问题
SpringApplication.run(application.class,args);
// 不接受外部临时参数
SpringApplication.run(application.class);
}
}package top.wabisabifag.quartz;
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.Scheduled;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class MyBean {
@Scheduled(cron = "0/1 * * * * ?")
public void print(){
// 获取线程名称
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+":spring task run 。。。");
}
}spring:
# 定时任务配置
task:
scheduling:
# 任务调度线程池大小 默认 1
pool:
size: 1
# 调度线程名称前缀 默认 scheduling-
thread-name-prefix: ssm_
shutdown:
# 线程池关闭时等待所有任务完成
await-termination: false
# 调度线程 关闭前最大等待时间,确保最后一定关闭
await-termination=period: 10s3. SpringBoot 整合 JavaMail
- SMTP(Simple Mail Transfer Protocol): 简单的邮件传输协议,用于发送电子邮件的传输协议
- POP3(Post Office Protocol -Version 3): 用于接收电子邮件的标准协议
- IMAP(Internat Mail Access Protocol): 互联网消息协议,POP3 替代协议
1. JavaMail(基础)
<!--JavaMail 整合-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-mail</artifactId>
</dependency>
spring:
# JavaMail 邮件
mail:
host: smtp.qq.com
username: 12345678@qq.com
# QQ邮箱 => 设置 => 账户 => POP3服务开启: 获取授权码 (付费功能)
password: zsaf45cocapackage top.wabisabifag;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import top.wabisabifag.service.SendMailService;
@SpringBootTest
public class SendMailTest {
@Autowired
private SendMailService sendMailService;
@Test
public void contextLoads(){
sendMailService.sendMail();
}
}package top.wabisabifag.service.impl;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.mail.SimpleMailMessage;
import org.springframework.mail.javamail.JavaMailSender;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import top.wabisabifag.service.SendMailService;
@Service
public class SendMaillServiceImpl implements SendMailService {
@Autowired
private JavaMailSender javaMailSender;
private String from = "12345678@qq.com"; /* 发送人*/
private String to = "12345678@126.com"; /* 接收人*/
private String subject = "测试邮件"; /* 标题*/
private String context = "测试邮件正文内容"; /* 正文*/
@Override
public void sendMail() {
SimpleMailMessage message = new SimpleMailMessage();
/* 替代发送者的邮箱账号,接收者信息有具体的信息*/
message.setFrom(from+"(好友:张伟)");
message.setTo(to);
message.setSubject(subject);
message.setText(context);
javaMailSender.send(message);
}
}package top.wabisabifag.service.impl;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.mail.SimpleMailMessage;
import org.springframework.mail.javamail.JavaMailSender;
import org.springframework.mail.javamail.MimeMailMessage;
import org.springframework.mail.javamail.MimeMessageHelper;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import top.wabisabifag.service.SendMailService;
import java.io.File;
@Service
public class SendMaillServiceImpl implements SendMailService {
@Autowired
private JavaMailSender javaMailSender;
private String from = "12345678@qq.com"; /* 发送人*/
private String to = "12345678@126.com"; /* 接收人*/
private String subject = "测试邮件"; /* 标题*/
private String context = "<a href='http://www.wabisabifag.top'>测试邮件正文内容</a>"; /* 正文*/
@Override
public void sendMail() {
try{
MimeMessage message = javaMailSender.createMimeMessage();
/* 1.添加附件功能: true*/
MimeMessageHelper helper = new MimeMessageHelper(message,true);
helper.setFrom(from+"(好友:张伟)");
helper.setTo(to);
helper.setSubject(subject);
/* 4.文档内容支持 HTML 格式*/
helper.setText(context,true);
/* 2.添加 附件*/
File file = new File("D:\\wabisabifag.jar");
File file2 = new File("D:\\学习资料.zip");
/* 3.附件名修改方式*/
helper.addAttachment(file.getName(),file);
helper.addAttachment("发给张总的素材.zip",file2);
javaMailSender.send(message);
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
3. 消息
- 生产者 消费者
- 消息队列
- 浏览器 ===>> 业务系统 ===>> MQ ===>> 子业务系统
1. 同步消息
2. 异步消息
1. JMS
JMS(Java Message Service): 一个规范,等同于JDBC 规范,提供消息服务的API接口
JMS 消息模型
- peer-2-peer: 点对点模型,消息发送到一个队列中,队列保存消息只能被一个消费者消费,或超时
- publish-subscribe: 发布订阅模型,消息被多消费者消费,生产者和消费者完全独立
JMS 消息种类
- TextMessage
- MapMessage
- BytesMessage (主要使用)
- StreamMessage
- ObjectMessage
- Message (只有消息和属性)
JMS 实现:
- ActiveMQ
- Redis
- HornetMQ
- RabbitMQ
2. AMQP
AMQP(advanced message queuing protocol): 一种协议(高级消息队列协议,消息代理规范)。会犯网络交换的数据格式,兼容JMS
- 特性
- 跨平台和语言
- 服务器供应商
- 生产者
AMQP 消息模型
- direct exchange
- fanout exchange
- topic exchange (主要)
- headers exchange
- system exchange
AMQP 消息种类
- byte[]
AMQP 实现:
- RabbitMQ
- StormMQ
- RockeMQ
3. MQTT
MQTT(Message Queueing Telemetry Transport) 消息队列遥测传输,专为小设备设计,物联网(IOT)生态系统主要成分之一
4. Kafka
Kafka 一种高吞吐量的分布式发布订阅消息系统,提供实时消息功能
3. 消息案例 — 模拟订单短信通知
package top.wabisabifag.service.impl;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import top.wabisabifag.service.MessageService;
import top.wabisabifag.service.OrderService;
@Service
public class OrderServiceImpl implements OrderService {
@Autowired
private MessageService messageService;
@Override
public void order(String id) {
/* 服务调用 处理各种业务*/
System.out.println("订单处理处理中。。。");
/* 短信消息处理*/
messageService.sendMessage(id);
System.out.println("订单处理完成");
}
}package top.wabisabifag.service.impl;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import top.wabisabifag.service.MessageService;
import java.util.ArrayList;
@Service
public class MessageServiceImpl implements MessageService {
private ArrayList<String> msgList = new ArrayList<>();
@Override
public void sendMessage(String id) {
System.out.println("待发送短信的订单已纳入处理队列: id"+id);
msgList.add(id);
}
@Override
public String doMessage() {
String id = msgList.remove(0);
System.out.println("已完成短信发送业务:id"+id);
return null;
}
}package top.wabisabifag.controller;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import top.wabisabifag.service.OrderService;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/orders")
public class OrderController {
@Autowired
private OrderService orderService;
@PostMapping("{id}")
public void Order(@PathVariable String id){
orderService.order(id);
}
}package top.wabisabifag.controller;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import top.wabisabifag.service.MessageService;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/msg")
public class MessageController {
@Autowired
private MessageService messageService;
@GetMapping
public String doMessage(){
String id = messageService.doMessage();
return id;
}
}1. ActiveMQ
安装运行
- 批处理运行: ../bin/win64/activemq.bat
- 安装: ../bin/win64/InstallService.bat
- 后台管理界面: 127.0.0.1:8161/ (password: admin)
- 服务端口: 127.0.0.1:61616/
- Spring 整合 ActiveMQ
<!--ActiveMQ 整合-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-activemq</artifactId>
</dependency>spring:
# ActiveMQ 消息
activemq:
broker-url: top://localhost:61616
jms:
# 发布订阅模型:true 点对点模型:false
pub-sub-domain: true
template:
default-destination: wabisabifagpackage top.wabisabifag.service.impl.activemq;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import top.wabisabifag.service.MessageService;
@Service
public class MessageServiceActivemqImpl implements MessageService {
@Autowired
private JmsMessagingTemplate messagingTemplate;
@Override
public void sendMessage(String id) {
System.out.println("待发送短信的订单已纳入处理队列: id"+id);
/* 设置队列名字 */
messagingTemplate.convertAndSend("order.queu.id",id);
}
@Override
public String doMessage() {
String id = messagingTemplate.receiveAndConvert(String.class);
System.out.println("已完成短信发送业务:id"+id);
return null;
}
}package top.wabisabifag.service.impl.activemq.listener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class MessageListener {
@JsmListener(destination = "order.queue.id")
public void recevi(String id){
System.out.println("已完成短信发送业务:id"+id);
}
}package top.wabisabifag.service.impl.activemq.listener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class MessageListener {
@JsmListener(destination = "order.queue.id")
@SendTo("order.other.queue.id")
public String recevi(String id){
System.out.println("已完成短信发送业务:id"+id);
return "new:"+ id;
}
}2. RabbitMQ
- RabbitMQ 基于Erlang 语言编写,需要安装 Erlang 并重启电脑
- 配置环境 ERLANG_HOME
- 管理员权限 ..\bin\rabbitmq-service.bat start
- 插件
- 查看 rabbitmq-plugins.bat list
- 开启 rabbitmq-plugins.bat enable rabbitmq_management
- 访问服务
- 管理后台端口 localhost:156772 (password: guest)
- 服务端口 localhost:5672
- direct exchange 直连交换机(消息模型)
direct exchange (消息模型)--><dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-amqp</artifactId> </dependency>
spring:
# RabbitMQ
rabbitmq:
host: localhost
# 服务端口 管理:15672
port: 5672package top.wabisabifag.service.impl.rabbitmq.direct.config;
import org.elasticsearch.common.inject.internal.BindingBuilder;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import javax.naming.Binding;
import java.util.Queue;
@Configuration
public class RabbitConfigDirect {
@Bean /* 消息队列*/
public Queue directQueue(){
/* 1.是否持久化 2.当前消息队列是否连接专用 3.是否删除*/
return new Queue("direct_queue",true,false,false);
}
@Bean /* 消息队列*/
public Queue directQueue2(){
return new Queue("direct_queue2");
}
@Bean /* 交换机*/
public DirectExchange directExchange(){
return new DirectExchange("directExchange");
}
@Bean /* 绑定消息队列和交换机*/
public Binding bindingDirect(){
return BindingBuilder.bind(directQueue()).to(directExchange()).with("direct");
}
@Bean /* 绑定消息队列和交换机*/
public Binding bindingDirect2(){
return BindingBuilder.bind(directQueue2()).to(directExchange()).with("direct2");
}
}package top.wabisabifag.service.impl.rabbitmq.direct;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import top.wabisabifag.service.MessageService;
@Service
public class MessageServiceRabbitmqDirectImpl implements MessageService {
@Autowired
private AmqpTemplate amqpTemplate;
@Override
public void sendMessage(String id) {
System.out.println("待发送短信的订单已纳入处理队列(rabbitmq direct):id"+id);
/* 明确消息模型*/
amqpTemplate.convertAndSend("directExchange","direct",id);
}
@Override
public String doMessage() {
return null;
}
}package top.wabisabifag.service.impl.rabbitmq.direct.listener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class MessageListener {
@RabbitListener(queue="direct_queue")
public void recive(String id){
System.out.println("待发送短信的订单已纳入处理队列(rabbitmq direct):id"+id);
}
}- topic exchange 主题交换机(消息模型)
package top.wabisabifag.service.impl.rabbitmq.topic.config;
import org.elasticsearch.common.inject.internal.BindingBuilder;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import javax.naming.Binding;
import java.util.Queue;
@Configuration
public class RabbitConfigTopic {
@Bean /* 消息队列*/
public Queue topicQueue(){
/* 1.是否持久化 2.当前消息队列是否连接专用 3.是否删除*/
return new Queue("topic_queue",true,false,false);
}
@Bean /* 消息队列*/
public Queue topictQueue2(){
return new Queue("topic_queue2");
}
@Bean /* 交换机*/
public TopicExchange topicExchange(){
return new TopicExchange("topicExchange");
}
/* 一次队列消息多次匹配*/
@Bean /* 绑定消息队列和交换机*/
public Binding bindingTopic(){
return BindingBuilder.bind(topicQueue()).to(topicExchange()).with("topic.*.id");
}
@Bean /* 绑定消息队列和交换机*/
public Binding bindingTopic2(){
return BindingBuilder.bind(topicQueue2()).to(topicExchange()).with("topic.order.*");
}
}package top.wabisabifag.service.impl.rabbitmq.topic.listener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class MessageListener {
@RabbitListener(queue="topic_queue")
public void recive(String id){
System.out.println("待发送短信的订单已纳入处理队列(rabbitmq direct):id"+id);
}
}package top.wabisabifag.service.impl.rabbitmq.topic;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import top.wabisabifag.service.MessageService;
@Service
public class MessageServiceRabbitmqTopicImpl implements MessageService {
@Autowired
private AmqpTemplate amqpTemplate;
@Override
public void sendMessage(String id) {
System.out.println("待发送短信的订单已纳入处理队列(rabbitmq topic):id"+id);
/* 明确消息模型*/ /*topic exchange 的特点*/
/* 一次队列消息多次匹配*/
amqpTemplate.convertAndSend("topicExchange","topic.order.id",id);
}
@Override
public String doMessage() {
return null;
}
}- 特性: 一个生产者,可产生多个消息队列,然后消费者通过routingkey去匹配生产者的routingkey
- 绑定键匹配规则
3. RocketMQ
- RocketMQ 下载地址
- 环境配置
- ROCKETMQ_HOME
- PATH
- NAMESRV_ADDR
- 访问服务
- 服务端口: 9876
- 管理端口: 127.0.0.1:9876
- 启动服务器
- mqnamesrv.cmd
- mqbroker.cmd
- RocketMq 整合
<!--rocketmq-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.rocketmq</groupId>
<artifactId>rockemq-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>2.2.1</version>
</dependency># rocketmq 消息
rocketmq:
name-server: localhost:9876
# 默认的生产者所属组
producer:
group: group_rocketmqpackage top.wabisabifag.service.impl.rocketmq;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import top.wabisabifag.service.MessageService;
@Service
public class MessageServiceRocketmqImpl implements MessageService {
@Autowired
private RocketMQTemplate rocketMQTemplate;
@Override
public void sendMessage(String id) {
System.out.println("待发送短信的订单已纳入处理队列(rabbitmq topic):id"+id);
//rocketMQTemplate.convertAndSend("order_id",id);
/* 异步发送消息队列*/
SendCallback callback = new SendCallback(){
@Override
public void onSuccess(SendResult sendResult){
System.out.println("消息发送成功");
}
@Override
public void onException(Throwable e){
System.out.println("消息发送失败");
}
};
rocketMQTemplate.convertAndSend("order_id",id);
}
@Override
public String doMessage() {
return null;
}
}package top.wabisabifag.service.impl.rocketmq.listener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
@RocketMQMessageListener(topic = "order_id",consumerGroup = "group_rocketmq")
public class MessageListener implements RocketMqListener{
@Override
public void onMessage(String id){
System.out.println("待发送短信的订单已纳入处理队列(roketmq):id"+id);
}
}4. Kafka
- Kafka
- 安装运行
- 启动zookeeper 注册器(默认端口:2181): zookeeper-server-start.bat ....\config\zookeeper.properties
- 启动kafka (默认端口:9092): kafka-server-start.bat ....\config\server.properties
- 创建topic: kafka-topic.bat –create –zookeeper localhost:2181 –replication-factor 1 –partition 1 –topic wabisabifag
- 查看topic: kafka-topics.bat –zookeeper 127.0.0.1:2181 –list
- 删除topic: kafka-topics.bat –delete –zookeeper localhost:2181 –topic wabisabifag
- 生产者功能测试: kafka-console-producer.bat –broker-list localhost:9092 –topic wabisabifag
- 消费者功能测试: kafka-console-consumer.bat –bootstrap-server localhost:9092 –topic wabisabifag –from-beginning
- Kafka 整合
<!--Kafka-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.kafka</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-kafka</artifactId>
</dependency>spring:
# Kafka
kafka:
bootstrap-servers: localhost:9092
consumer:
group-id: orderpackage top.wabisabifag.service.impl.kafka;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import top.wabisabifag.service.MessageService;
@Service
public class MessageServiceKafkaImpl implements MessageService {
@Autowired
private KafkaTemplate<String,String> kafkaTemplate;
@Override
public void sendMessage(String id) {
System.out.println("待发送短信的订单已纳入处理队列(Kafka):id"+id);
kafkaTemplate.send("wabisabifag",id);
}
@Override
public String doMessage() {
return null;
}
}package top.wabisabifag.service.impl.kafka.Listener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class MessageListener {
// 监听 消费有页面存入 kafka 的缓存数据
@KafkaListener(topics={"wabisabifag"})
public void onMessage(ConsumerRecord<String,String> record){
System.out.println("待发送短信的订单已纳入处理队列(Kafka):id"+record.value());
}
}4. 监控
1. 监控的意义
- 监控服务状态是否宕机
- 监控服务运行指标(内存,虚拟机,线程,请求等)
- 监控日志
- 管理服务
1. 监控的实施方式
- 显示监控信息的服务器: 用于获取服务信息,并显示对应的信息
- 运行的服务: 启动时,主动上报。告知监控服务器自己需要受到监控
2. 可视化监控平台
- Java 提供一个jmx方式获取的监控平台:cmd命令行 输入: jconsole
- 也可以通过 http 的 web 程序获取
1. SpringBoot Admin
SpringBoot Admin 文档 监控管理SpringBoot 应用程序。客服端注册到服务端后,通过 HTTP 请求方式,服务端定期从客服端获取对应信息,通过UI界面战士对应信息
<!--监控 服务端-->
<dependency>
<groupId>de.codecentric</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-admin-starter-server</artifactId>
<!--和SpringBoot版本对应-->
<version>2.4.5</version>
</dependency>
<!--监控 客服端-->
<dependency>
<groupId>de.codecentric</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-admin-starter-client</artifactId>
<version>2.4.5</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency># 向服务端 提交监控
spring:
boot:
admin:
client:
url: http://localhost:8080
management:
# 端点功能的开关控制
endpoint:
# 必须对外开放的
health:
show-details: always
# 不对外展示 端口
info:
enabled: false
# 端点功能的暴露
endpoints:
# 在web页面能获取的端口
web:
exposure:
include: "*"
# 启用所有端口
enabled-by-default: true@SpringBootApplication
/* 开启监控*/
@EnableAdminServer
public class application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 线程安全问题
SpringApplication.run(application.class,args);
// 不接受外部临时参数
SpringApplication.run(application.class);
}
}3. 监控原理
- Actuator 提供SpringBoot 生产就绪功能,通过端点的配置与访问获取端点信息(spring-boot-admin-starter-client 提供spring-boot-admin-starter-actuator)
- 端点描述一组监控信息。SpringBoot 提供多个内置端点,也可以根据需要自定义端点信息
- 访问当前应用的所有端点信息: /actuator
- 访问端点详细信息: /actuator/端点名称
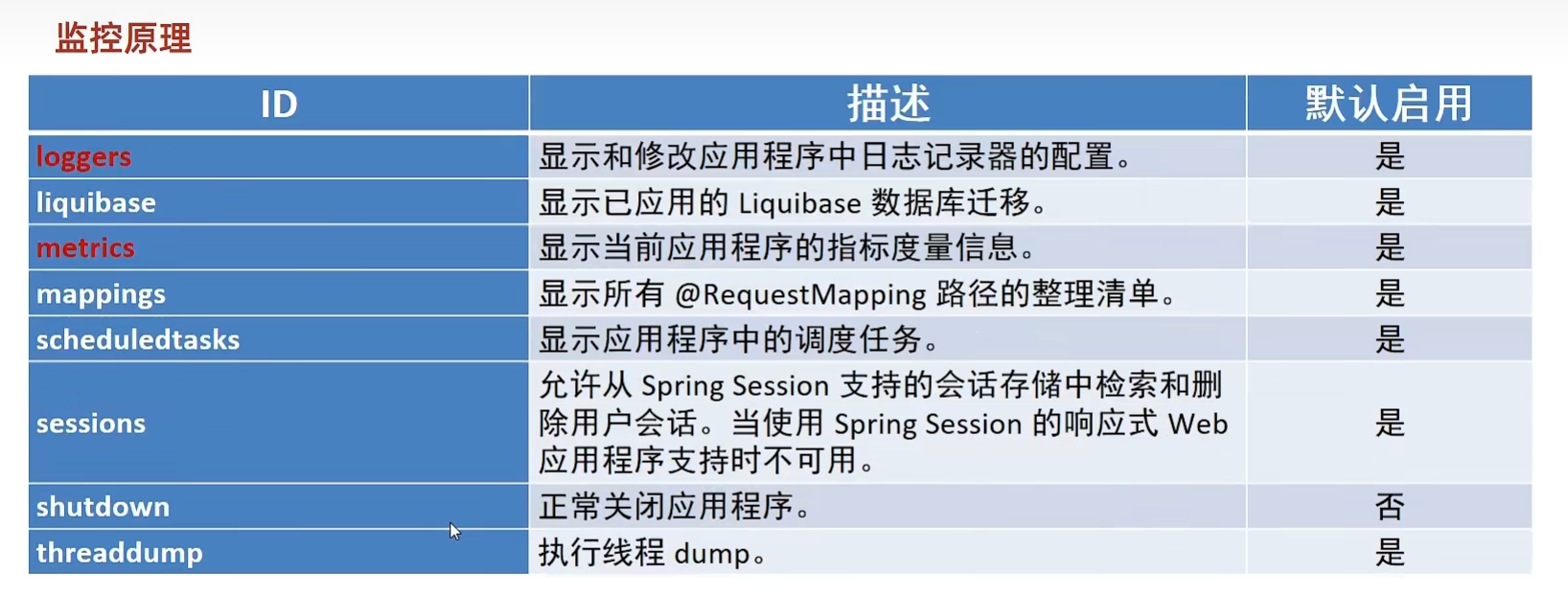

4. 自定义监控指标
info 端点指标控制
info: # 静态信息 # 映射项目名称 webName: @project.artifactId@ version: @project.version@ author: wabisabifagpackage top.wabisabifag.actuator; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; import java.util.HashMap; @Component public class InfoConfig implements InfoContributor{ @Override public void contribute(Info.Builder builder){ // withDetail() 单值加载 builder.withDetail("runtime",System.currentTimeMillis()); // withDetails() 多值加载 Map infoMap = new HashMap(); infoMap.put("buildTime","2006"); builder.withDetails(infoMap); } }health 端点指标控制
package top.wabisabifag.actuator; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; import java.util.HashMap; @Component public class HealthConfig extends AbstractHealthIndocator{ @Override protected void doHealthCheck(Health.Builder builder) throws Exception{ boolean condition = true; if (condition){ // 设置 health 的状态 builder.status(Status.UP); /*builder.unknown(); builder.outService(); builder.down();*/ builder.withDetail("runtime",System.currentTimeMillis()); Map infoMap = new HashMap(); infoMap.put("buildTime","2006"); builder.withDetails(infoMap); }else { builder.withDetail("上线了吗?","你做梦"); builder.down(); } } }metrics 端点指标控制
@Service public class BookServiceImpl extends ServiceImpl<BookDao Book> implements IBookService{ private Counter counter; public BookServiceImpl(MeterRegistry meterRegistry){ // 监控的名称 cunter = meterRegistry.counter("用户付费操作次数:"); } @Override public boolean delete(Integer id){ // 原子递增 counter.increment(); return bookDao.deleteById(id) > 0; } }自定义监控指标
package top.wabisabifag.actuator; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; import java.util.HashMap; @Component /* 声明端点名 id:访问名称 是否默认开启*/ @Endpoint(id="pay",enableByDefault=true) public class PayEndpoint { /* 注解功能: 端点读取时调用该方法*/ @ReadOperation public Object getPay(){ // 调用业务操作 获取支付相关信息结果,return一个可转换为 json 数据的值 Map payMap = new HashMap(); payMap.put("vip 1","10"); payMap.put("vip 2","100"); payMap.put("vip 3","韭菜嘎嘎多"); return payMap; } }
2. Docker
Docker 官方安装文档 是一个快速构建、运行、管理应用工具
1. 传统 Linux 安装 MySQL 数据库
1. 准备工作
1. 查看系统环境
使用 lable lsb_release -a 命令查看Linux 系统版本,便于下载MySql安装包时选择对应的 OS version
2. 下载MySQL 安装包
下载MySQL,选择 OS Version 以及 MySQL安装包
解压命令:tar -xf packageName -C /user/local/…
2. 安装
1. 卸载默认数据库 MariaDB
- 查看已存在的数据库:
yum list installed | grep mariadb && yum list installed | grep mysql - 卸载:
yum -y remove -mariadb-libs.x86_64 - 按顺序安装以下几个文件:
在此安装过程中,遇到了如下问题:rpm -ivh mysql-community-common-8.0.29-1.el7.x86_64.rpm rpm -ivh mysql-community-client-plugins-8.0.29-1.el7.x86_64.rpm rpm -ivh mysql-community-libs-8.0.29-1.el7.x86_64.rpm rpm -ivh mysql-community-libs-compat-8.0.29-1.el7.x86_64.rpm rpm -ivh mysql-community-devel-8.0.29-1.el7.x86_64.rpm rpm -ivh mysql-community-client-8.0.29-1.el7.x86_64.rpm rpm -ivh mysql-community-icu-data-files-8.0.29-1.el7.x86_64.rpm rpm -ivh mysql-community-server-8.0.29-1.el7.x86_64.rpm
- mysql-community-devel 安装失败
- 解决方法:
- 安装依赖 openssl-devel:yum install openssl-devel -y
- 安装失败一般是由包依赖引起的,安装对应的依赖包即可
查看安装完成后的安装包
查看已完成的安装完:rpm -qa | grep mysql初始化MySQL服务
修改数据库目录与文件(默认/var/lib/mysql下)的所有者为mysql用户:mysqld --initialize --user=mysql
该命令执行后会生成一个root的临时密码,在 /var/log/mysqld.log 文件中:
grep "password" /var/log/mysqld.log启动MySQL服务
service mysqld start验证
输入刚才找到的临时密码登录命令行操作mysql -uroot -p验证成功。
2.Docke 安装
1. 配置Docker 的 yum 库
安装yum工具:
yum install -y yum-utils安装完成执行命令,配置Docker 的 yum 源:
yum-config-manager --add-repo https://download.docker.com/linux/centos/docker-ce.repo2. 安装 Docker
yum install -y docker-ce docker-ce-cli comtainerd.io docker-buildx-plugin docker-compose-plugin- 版本验证:
docker -v # 启动 docker systemctl start docker systemctl stop docker # 设置开启自启动 systemctl restart docker # 执行docker.ps 命令检验 docker ps # 启动守护进程 docker images
3. 配置镜像加速
4. Docker 一键部署MySQL
自动搜索下载应用镜像,创建一个隔离环境的容器
多个创建用 docker ps 可以检查多个运行应用
- 一键部署MySQL 命令
docker run -d --name wabisabifag -p 3306:3306 -e MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD=123 -e TZ=Asia/Shanghai -v /root/mysql/data:/var/lib/mysql -v /root/mysql/init:/docker-entrypoint-initdb.d -v /root/mysql/config:/etc/mysql/conf.d mysql:5.1.47
- docker run: 创建运行容器 -d 让容器在后台运行
- –name: 唯一名称
- -p:映射端口,宿主机端口:容器端口
- -e:设置MySQL的 Key=Value环境变量
- mysq:指定镜像名(不写默认最新)
3. 常见命令
# 镜像仓库
docker pull docker push
# 本地镜像
docker images docker rmi #删除镜像
# DOCKERFILE
docker build
docker save docker load
# 容器
docker run #启动并创建文件
docker start
docker stop
docker ps # 查看运行状态
docker rm # 删除容器
docker logs # 查看容器日志
docker exec # 容器修改4. 查看DockerHub,拉取nginx 镜像,创建运行Nginx容器
在DockerHub搜索Nginx镜像,查看镜像名称
拉去Nginx 镜像: docker pull nginx
查看本地镜像列表: docker images
- 保存打包至本地:docker save -o nginx.tar nginx:latest
- 读取容器: docker load -i nginx.tar
创建并运行Nginx 容器:docker run -d –name nginx -p 80:80 nginx
查看运行的容器: docker ps
查看所有容器:docker ps -a
停止容器: docker stop nginx
再启动容器:docker start nginx
进入Nginx容器:docker exec -it nginx bash /docker exec -it mysql mysql -uroot -p
- 退出命令:exit
删除容器(运行时强行删除):docker rm mysql -f
5. 命令别名
vi ~/.bashrc
# 简化执行命令
alias dps='docker ps -format "table{{.ID}}\t{{.Image}}\t{{.Ports}}\t{{.Status}}\t{{.Names}}"'
source ~/.ashrc6.数据卷
1. 数据卷挂载
数据卷(volume)是一个虚拟目录,容器内目录与宿主机目录之间映射的桥梁
- 创建Nginx容器,修改Nginx 容器内的html目录的index.html文件,查看变化(/user/share/nginx/htmml),挂在数据卷:
- docker run -d –name nginx -p 80:80 -v html:/user/share/nginx/htmml nginx
- docker volume inspect html
- 将静态资源部署到Nginx 的html目录
# 命令 说明
docker volume create 创建数据卷
docker volume ls 查看所有数据卷
docker volume rm 删除指定数据卷
docker volume inspect 查看某个数据卷的详情
docker volume prune 清除数据卷2. mysql容器的数据挂载
查看mysql容器,数据卷挂载(自动创建的匿名卷,当容器删除时Volume文件依然存在,但重配置容器容易文件丢失,且文件复制繁琐,所以手动挂载)
- docker inspect mysql
基于宿主机目录实现 MySQL 数据目录、配置文件、初始化脚本的挂载
docker run -d
–name wabisabifag \
-p 3306:3306
-e MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD=123
-e TZ=Asia/Shanghai
-v /root/mysql/data:/var/lib/mysql \
-v /root/mysql/init:/docker-entrypoint-initdb.d \
-v /root/mysql/config:/etc/mysql/conf.d \
mysql:5.7–network wabisabifag \
hm.cnf
[client]
default_character_set=utf8mb4
[mysql]
default_character_set=utf8mb4
[mysqld]
character_set_server=utf8mb4
collation_server=utf8mb4_unicode_ci
init_connect='SET NAMES utf8mb4'
7. 自定义镜像
1. 镜像结构
- 层(Layer)
添加安装包,依赖,配置等,每次操作都形成新的一层(每个操作压缩一个包) - 基础镜像(BaseImages)
应用依赖的系统函数库、环境、配置、文件等 - 入口(Entrypoint)
镜像运行入口,一般程序启动的脚本和参数
Dockerfile
Dockerfile 是一个文件夹,其中包含一个个指令(Instruction)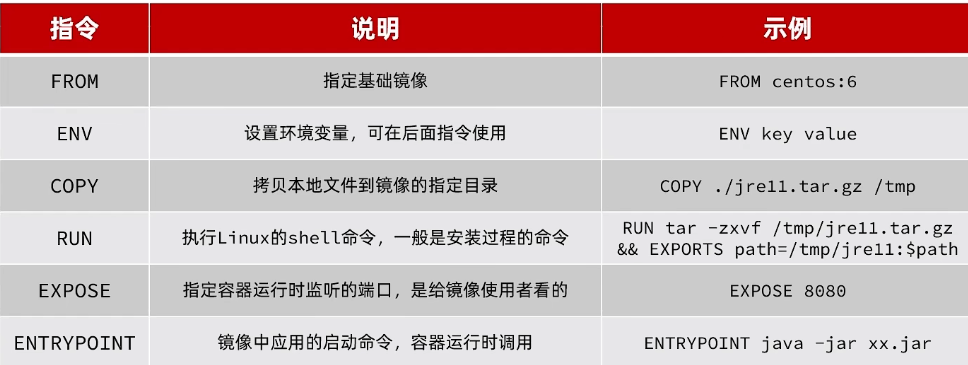
docker build -t myImage:1.0 .-t: 镜像名(格式:repository:tag)
. : 指定Dockerfile所在目录,如果就在当前目录,则指定为”.”
# 指定基础镜像
FROM ubuntu:16.04
# 配置环境变量,3DK的安装目录、容器内时区
ENV JAVA_DIR=/usr/local
# 拷贝jdk和java项目的包
COPY ./jdk8.tar.gz $JAVA_DIR/
COPY ./docker-demo.jar /tmp/app.jar
# 安装JDK
RUN cd $JAVA_DIR \ && tar -xf ./jdk8.tar.gz \
&& mv ./jdkl.8.0_144 ./java8
#配置环境变量
ENV JAVA_HOME=$JAVA_DIR/java8
ENV PATH=$PATH:$JAVA_HOME/bin
#入口,java项目的启动命令
ENTRYPOINT ["java", "-jar", "/app.jar"]# 基础镜像
FROM openjdk:11.0-jre-bister
# 拷贝jar贝
COPY docker-demo.jar /app.jar
# 入口
ENTRYTPOINT ["java", "-jar", "/app.jar"]8. 网络
- 默认情况所有容器以bridge方式连接到Docker的一个虚拟网桥上:
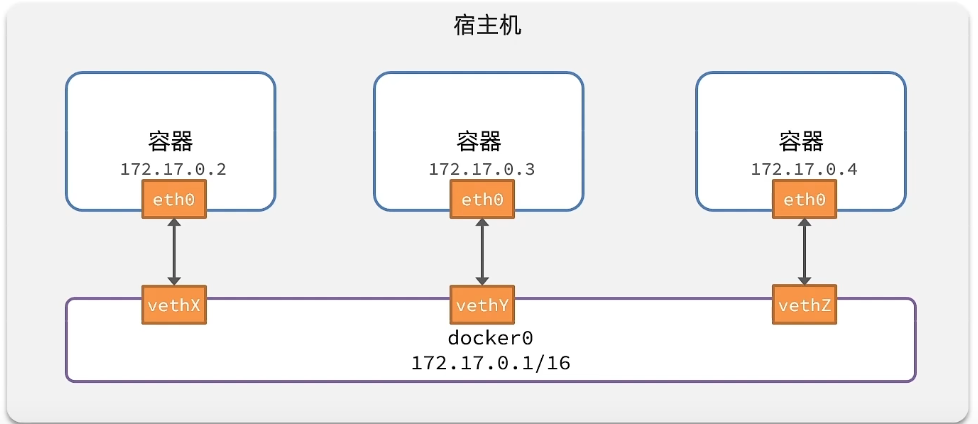
1. 容器互联
- 加入自定义网络容器才可以通过容器互相访问,Docker的网络操作命令如下:
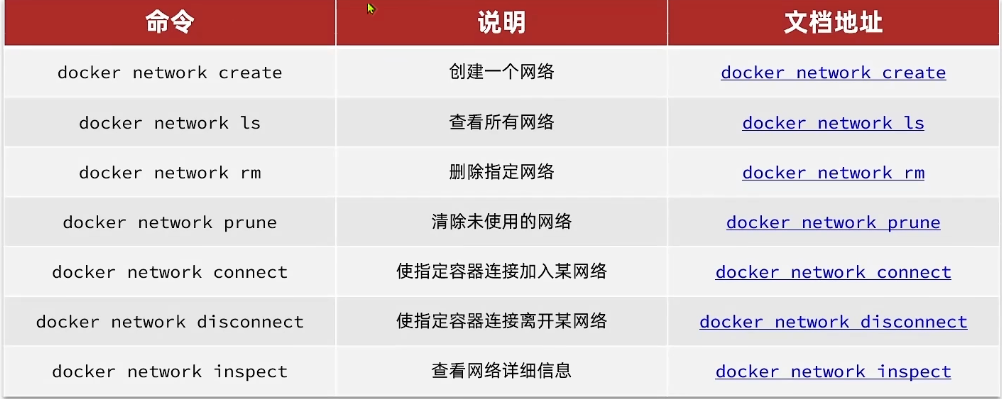
9. DockerCompose
Docker Compose 通过一个单独的docker-compose.yml模版文件(YAML格式)定义一组相关联的应用容器,帮助我们实现 多个相互关联的Docker容器的快速部署。
- 一键部署
- 集群部署
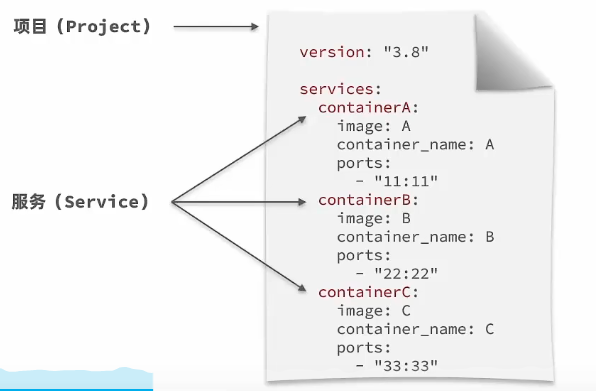
1. docker compose 命令格式
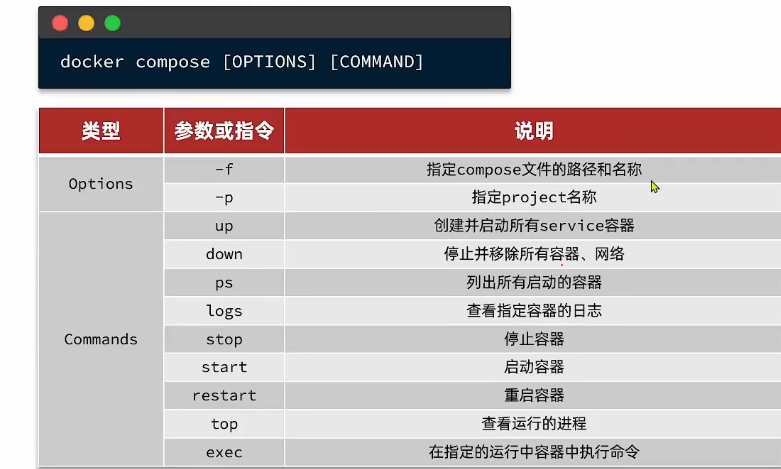
- 比较命令行和docker-compose.yml 文件
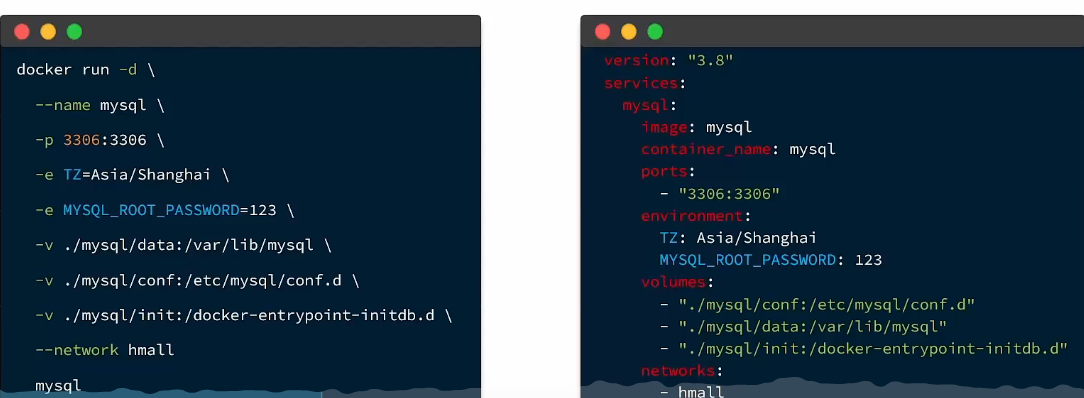
2. docker-compose.yml一键部署
docker compose up -d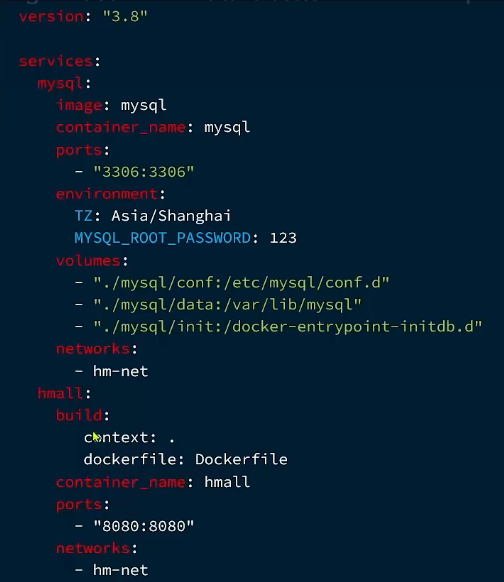
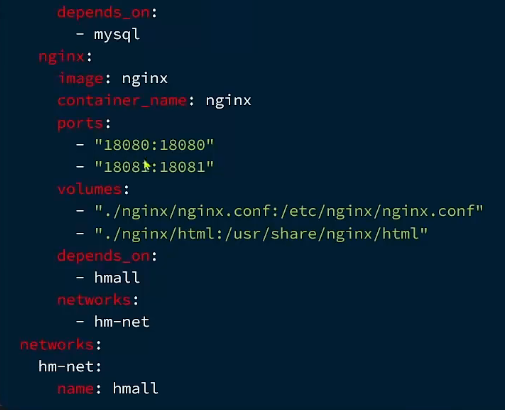
3.Redis
1.Redis 基础
1.初识Redis
1.认识NoSQL
- SQL
- 数据结构: 结构化
- 数据关联: 关系型
- 外键表关联
- 查询方式: SQL
- SELECT id FROM td_user WHERE id=1;
- 事务特性: ACID(安全)
- 扩展性: 垂直
- 使用场景:
- 数据结构固定
- 相关业务对数据安全性、一致性要求高
- NoSQL
- 数据结构: 非结构化
- key:value 键值对类型(Redis)
- Document 文档类型(MongoDB)
- Graph 图(Neo4j)
- 列类型(HBase)
- 数据关联: 非关系型
- 查询方式: 非SQL
- Redis: get user:1
- MongDB: db.users.find({_id:1})
- elasticsearch GET http://localhost:9200/users/1
- 事务特性: BASE
- 扩展性: 水平
- 使用场景:
- 数据结构不固定
- 相关业务对数据安全性、一致性要求不高
- 对性能要求高
- 数据结构: 非结构化
2.认识Redis
Remote Dictionary Server(远程词典服务器)是一个基于内存的键值型单线程NoSQL数据库。
- 特征:
- 键值型,value支持多种不同数据结构,功能丰富
- 单线程,每个命令具备原子性
- 低延迟,速度快(基于内存、IO多路复用、良好的编码)
- 支持数据持久化
- 支持主从集群、分片集群
- 支持多语言客户端
3.安装Redis
1.Redis指定配置启动
// 备份源文件
cp redis.conf redis.conf.bck
// 监听地址:127.0.0.1 本地访问 修改为 0.0.0.0 可以在任意IP访问
bind 0.0.0.0
# 守护进程,修改为 yes 后台运行
daemonize yes
# 密码,设置后访问 Redis 必须输入密码
requirepass 123456
# 设置数据库数量,默认16,编号0-15
database 1
# 最大使用内存
maxmemory 512mb
# 日志文件、默认为空,可指定日志文件名
logfile "redis.log"2.开机自启
# 新建系统服务文件
vi /etc/systemd/system/redis.service
######## 文件
[Unit]
Description=redis-server
After=network.target
[Service]
Type=forking
ExecStart=/usr/local/bin/redis-server /usr/local/src/redis-6.2.6/redis.conf
PrivateTmp=true
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
# 重载系统服务
systemctl daemon-reload
# 启动Redis
systemctl start redis
# 开机自启
systemctl enable redis3.Redis客服端
1.命令行客户端
redis-cli [options] [commonds]
- options
- -h 127.0.0.1: 指定连接的Redis节点的IP地址
- -p 6379: 指定要连接的Redis节点的端口(不建议)
- 在连接Redis后 通过: AUTH 123321 (与Redis服务端做心跳测试)
- -a 123456: 指定Redis访问密码
- commonds
- ping: 与Redis服务端做心跳测试。服务端正常返回 pong。不指定commond时,会进入 redis-cli的交互控制台
2.图形化桌面客户端
- GitHub用户编写的Redis图形化桌面客户端(未提供Windows安装包,需要付费使用)
- 提供免费的Redis图形化桌面客户端
# 更换Redis库名
select 0
# 存 取 数据操作
set get2.Redis常见命令
1.5种常见数据结构
1.Redis数据结构
- 基本类型
- String
- Hash:
- {name:”jack”,age:21}
- List:
- [A -> B ->C]
- Set(无序,不可重复):
- {A,B,C}
- SortedSet:
- {A:1,B:2,C:3}
- 特殊类型
- GEO:
- {A:(120.3,30.5)}
- BitMap:
- 0110110101110101011
- HyperLog:
- 0110110101110101011
- GEO:
2.Redis通用命令(Keys)
- KEYS 查看所有符合模版
- KEYS * 模糊查询
- DEL 删除一个或多个key值
- DEL *
- EXISTS 判断key存在
- EXPIRE 设置key的有效期
- EXPIRE age 20
- TTL 查看key剩余有效期(-1:永久有效)
- TTL age
通过help [command] 查看命令具体使用方法
3.String类型
- String类型分为三类
- String:字符串(<512m)
- int:可做自增自减操作
- float:可做自增自减操作
底层都是字节数据形式存储,但是编码方式不同。
字符串类型的最大空间不超过512m
1.String的常见命令有:
SET:添加或者修改已经存在的一个String类型的键值对
GET:根据key获取String类型的value
MSET:批量添加多个String类型的键值对
MGET:根据多个key获取多个String类型的value
INCR:让一个整型的key自增1
DECR:让一个整型的key自减1
INCRBY:让一个整型的key自增并指定步长,例如:incrby num 2让num值自增2
INCRBYFLOAT:让一个浮点类型的数字自增并指定步长
SETNX:新增一个String类型的键值对,前提是这个key不存在,否则不执行
SETEX:新增一个String类型的键值对,并且指定有效期
2.key的结构
Redis允许多个单词形成层级结构,多个单词间用’:’,格式如下:
- 项目名:业务名:类型:id
- user相关key: wabisabifag:user:1
- vaule: get {“id”:1,”name”:”Jack”,”age”:21}
- video相关key: wabisabifag:video:1
- value: {“id”:1,”name”:”OPPO”,”price”:2100}
# 注意 value 用 单引号 set wabisabifag:user:1 '{"id":1,"name":"Jack","age":21}' GET wabisabifag:user:1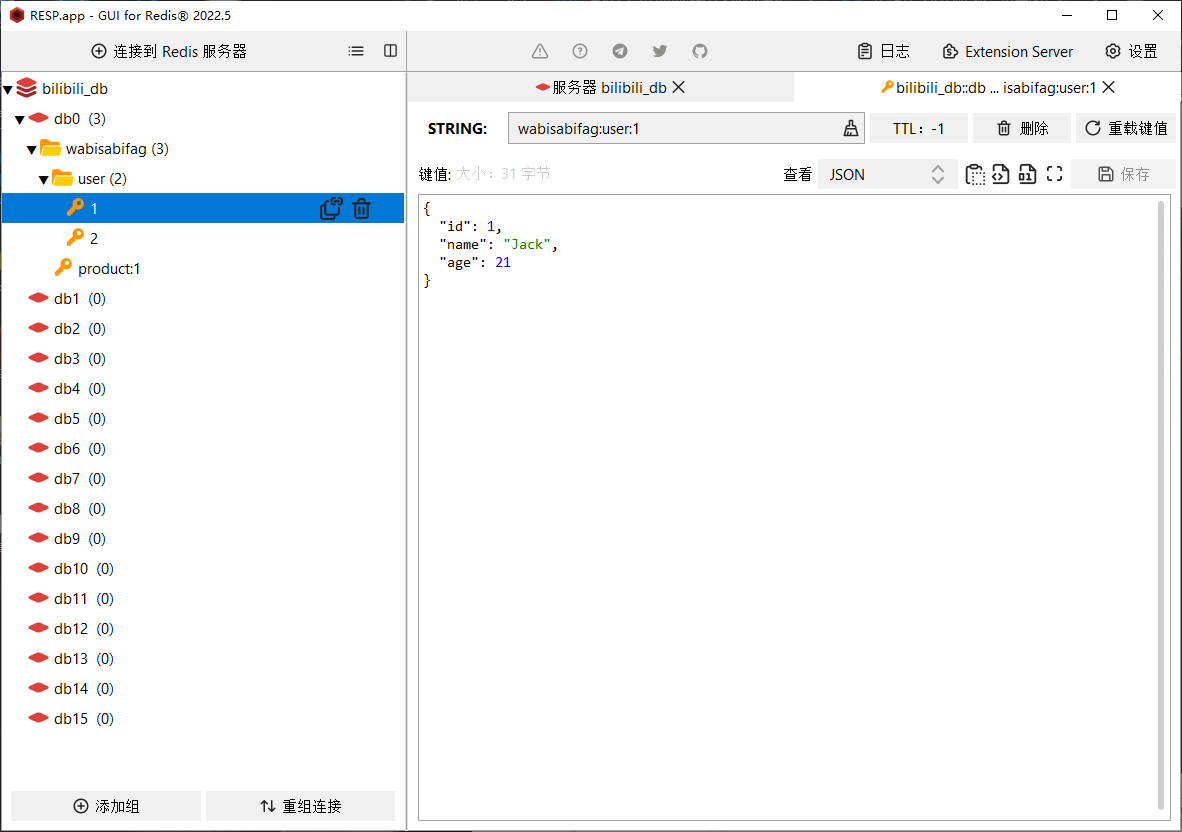
- value: {“id”:1,”name”:”OPPO”,”price”:2100}
- user相关key: wabisabifag:user:1
4.Hash类型
Hash类型(散列),value是一个无序字典,类似java的HashMap结构。
- String结构对象序列化为JSON字符串后存储,当修改对象某个字段时不方便
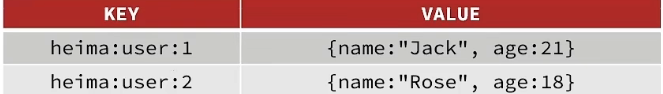
- Hash结构可以将对象的每个字段独立存储,可针对单个字段做CRUD
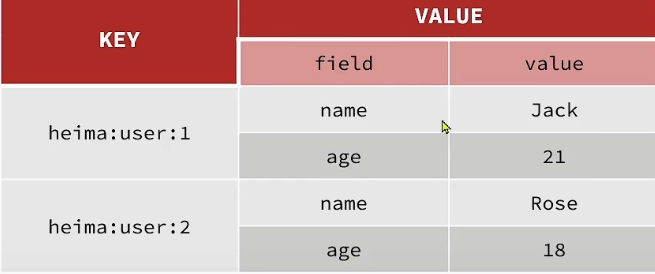
1.Hash的常见命令有:
HSET key field value:添加或者修改hash类型key的field的值
HGET key field:获取一个 hash 类型 key 的 field 的值
HMSET:批量添力口多个hash类型key的field的值 a
HMGET:批量获取多个hash类型key的field的值
HGETALL:获取一个hash类型的key中的所有的field和value
HKEYS:获取一个hash类型的key中的所有的field
HVALS:获取一个hash类型的key中的所有的value
HINCRBY:让一个hash类型key的字段值自增并指定步长
- HINCRBY wabisabi:user:1 age -2
HSETNX:添加一个hash类型的key的field值,前提是这个field不存在
HMSET wabisabifag:user:1 name wabisabifag age 20 gender man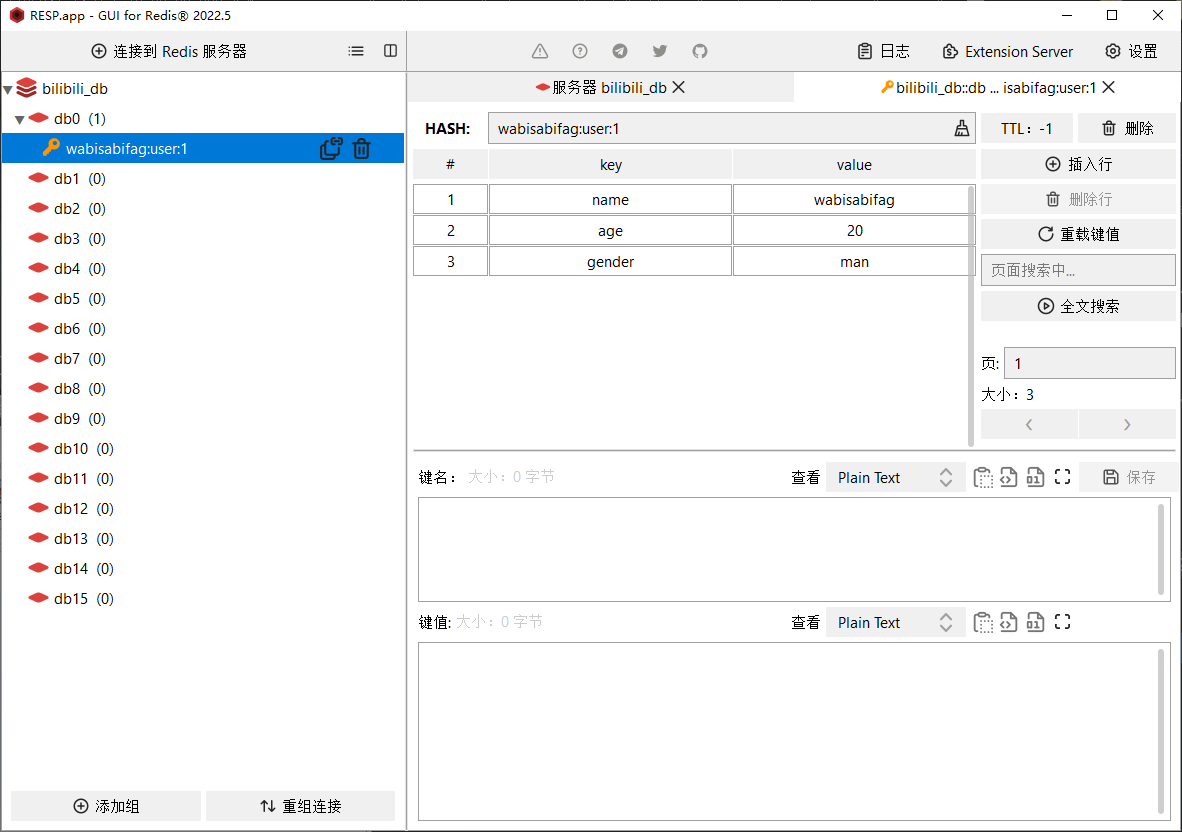
5.List类型
Redis的List类型是一个双向链表结构,可以双向检索
1.List特征
- 有序
- 元素可重复
- 插入和删除快
- 查询速度一般
2.List的常见命令
LPUSH key element… :向列表左侧插入一个或多个元素
LPOP key:移除并返回列表左侧的第一个元素,没有则返回nil
RPUSH key element… :向列表右侧插入一个或多个元素
RPOP key:移除并返回列表右侧的第一个元素
LRANGE key star end:返回一段角标范围内的所有元素
BLPOP和BRPOP:与LPOP和RPOP类似,只不过在没有元素时等待指定时间,而不是直接返回而
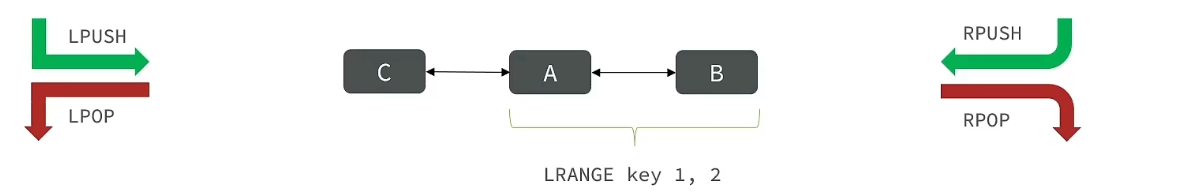
# 阻塞式获取等待(user2不存在,等待时间100s)
BLPOP user2 1003.模拟 栈 功能
- List结构模拟栈
- 入口和出口在同一边
- List结构模拟队列
- 入口和出口不在同一边
- List结构模拟阻塞队列
- 入口和出口不在同一边
- 出队时采用BLPOP或BRPOP
6.Set类型
Redis的Set结构是一个value为null的HashMap,应为是一个hash表,因此具备HashSet类似特征(社交关系应用)
- 无序
- 元素不可重复
- 查询快
- 支持交集、并集、差集等功能
1.Set的常见命令
SADD key member…:向set中添加一个或多个元素
SREM key member…:移除set中的指定元素
SCARD key:返回set中元素的个数
SMEMBERS:获取set中的所有元素
SISMEMBER key member:判断一个元素是否存在于set中
SINTER keyl key2 …:求keyl与key2的交集
SDIFF keyl key2 …:求keyl 与key2的差集
SUNION keyl key2 求keyl和key2的并集
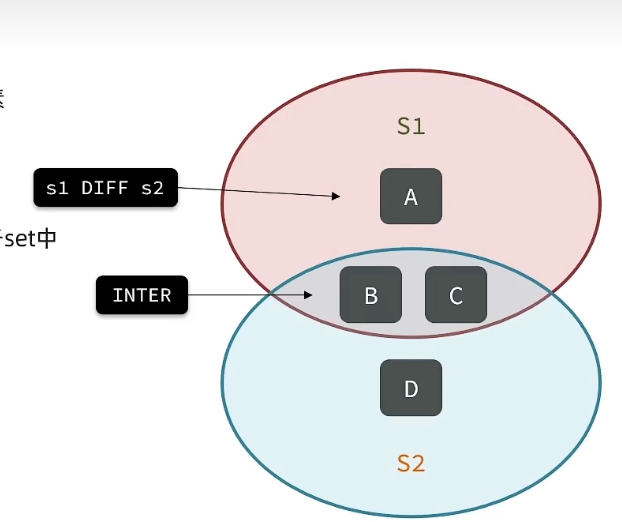
7.SortedSet类型
Redis的SortedSet是一个可排序的set集合
1.SortedSet特性
SortedSet中的每一个元素都带一个score属性,基于score属性对元素排序,底层的实现是一个跳表(SkipList)加Hash表
2.SortedSet的常见命令
ZADD key score member:添加一个或多个元素到sorted set,如果已经存在则更新其score值
ZREM key member:删除sorted set中的一个指定元素
ZSCORE key member:获取sorted set中的指定元素的score值
ZRANK key member:获取sorted set中的指定元素的排名
ZCARD key:获取sorted set中的元素个数
ZCOUNT key min max:统计score值在给定范围内的所有元素的个数
ZINCRBY key increment member:让sorted set中的指定元素自增,步长为指定的increment值
ZRANGE key min max:按照score排序后,获取指定排名范围内的元素
ZRANGEBYSCORE key min max:按照score排序后,获取指定score范围内的元素
ZDIFF、ZINTER. ZUNION:求差集、交集、并集
注意: 排名默认升序,降序排序格式 Z+rev+语法。例如: ZREVINCRBY key increment member
3.Redis的Java客户端
在Redis官网中提供各种语言Redis的客户端
1.Jedis客户端
Spring Data Redis 整合Jedis和lettuce
- Jedis以Redis命令作为方法名称,学习成本低,简单实用。但是Jedis实例线程不安全,多线程环境下需要基于连接池使用
- lettuce基于Netty实现,支持同步、异步、和响应式编程方式,线程安全。支持Redis的哨兵模式、集群模式和管道模式
- Redisson是基于Redis实现的分布式、可伸缩的Java数据结构集合,包含Map、Queue、Lock、Semaphore、AtomicLong等功能
1.Springboot整合Jedis
<!--jedis-->
<dependency>
<groupId>redis.clients</groupId>
artifactId>jedis</artifactId>
</dependency>package top.wabisabifag.test;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.AfterEach;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.BeforeEach;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import redis.clients.jedis.Jedis;
import top.wabisabifag.util.JedisConnectionFactory;
public class JedisTest {
private RedisProperties.Jedis jedis;
@BeforeEach
void setUp(){
// 1.建立连接
jedis = new RedisProperties.Jedis();
// 2.设置密码
jedis.auth("123456");
// 3.选择库
jedis.select(0);
}
@Test
void testString(){
// 存入数据
String result = jedis.set("name","Tigger");
System.out.println("result="+result);
// 获取数据
String name = jedis.get("name");
System.out.println("name="+name);
}
@Test
void testHash(){
//插入Hash数据
jedis.hset("user:1","name","jack");
jedis.hset("user:1","age","20");
// 获取
Map<String,String> map=jedis.hgetAll("user:1");
}
@AfterEach
void tearDown(){
// 4. 关闭资源
if (jedis!=null){
jedis.close();
}
}
}package top.wabisabifag.util;
import redis.clients.jedis.Jedis;
import redis.clients.jedis.JedisPool;
import redis.clients.jedis.JedisPoolConfig;
public class JedisConnectionFactory {
private static final JedisPool jedisPool;
static {
// 配置连接池
JedisPoolConfig poolConfig = new JedisPoolConfig();
poolConfig.setMaxTotal(8);
poolConfig.setMaxIdle(8);
poolConfig.setMaxIdle(0);
poolConfig.setMaxWaitMillis(100);
// 创建连接池对象
jedisPool = new JedisPool(poolConfig,
"192.168.0.0.1",6379,100,"123456");
}
public static Jedis getJedis(){
return jedisPool.getResource();
}
}package top.wabisabifag.test;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.AfterEach;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.BeforeEach;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import redis.clients.jedis.Jedis;
import top.wabisabifag.util.JedisConnectionFactory;
import java.util.Map;
public class JedisTest {
private Jedis jedis;
@BeforeEach
void setUp(){
// 1.建立连接
jedis = JedisConnectionFactory.getJedis();
// 2.设置密码
jedis.auth("123456");
// 3.选择库
jedis.select(0);
}
@Test
void testString(){
// 存入数据
String result = jedis.set("name","Tigger");
System.out.println("result="+result);
// 获取数据
String name = jedis.get("name");
System.out.println("name="+name);
}
@Test
void testHash(){
//插入Hash数据
jedis.hset("user:1","name","jack");
jedis.hset("user:1","age","20");
// 获取
Map<String,String> map=jedis.hgetAll("user:1");
}
@AfterEach
void tearDown(){
// 4. 关闭资源
if (jedis!=null){
jedis.close();
}
}
}
2.SpringDataRedis 客户端
SpringData是Spring中数据操作的模块,包含对各种数据库的集成,其中Redis的集成模块叫做SpringDataRedis
- 提供了对不同Redis客户端的整耳(Lettuce和Jedis)
- 提供了 RedisTemplate 统一API 来操作 Redis
- 支持Redis的发布订阅模型
- 支持Redis哨兵和Redis集群
- 支持基于Lettuce的响应式编程
- 支持基于JDK、JSON、字符串、Spring对象的数据序列化及反序列化
- 支持基于Rudis的JDKCoUection实现
1.RedisTemplate工具类
SpringDataRedis中提供了RedisTemplate工具类,其中封装了各种对Redis的操作。并且将不同数据类型的操作API封 装到了不同的类型中:
API
rednsTemplate.opsForValue()
- ValueOperations 操作String类型数据
redisTemplate.opsForHash()
- Hashoperations 操作Hash类型数据
red-isTemplate.opsForList()
- Listoperations 操作List类型数据
redisTemplate.opsForSet ()
- SetOperations 操作Set类型数据
redisTemplate.opsForZSet()
- ZSetOperations 操作SortedSet类型数据
redisTemplate 通用的命令
1.SpringBoot 配置序列化类
package top.wabisabifag.config;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonAutoDetect;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonInclude;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonTypeInfo;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.PropertyAccessor;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.DeserializationFeature;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.MapperFeature;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.SerializationFeature;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.jsontype.impl.LaissezFaireSubTypeValidator;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.RedisConnectionFactory;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.StringRedisSerializer;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.TimeZone;
@Configuration
public class MyRedisConfig {
@Resource
private RedisConnectionFactory factory;
@Bean
public RedisTemplate redisTemplate(){
RedisTemplate<String,Object> redisTemplate = new RedisTemplate<>();
redisTemplate.setConnectionFactory(factory);
redisTemplate.setKeySerializer(new StringRedisSerializer());
// String 类型序列化 json
Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer<Object> serializer = new Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer<>(Object.class);
redisTemplate.setValueSerializer(serializer);
ObjectMapper om = new ObjectMapper();
om.setVisibility(PropertyAccessor.ALL, JsonAutoDetect.Visibility.ANY);
om.setDateFormat(new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss"));
om.setTimeZone(TimeZone.getDefault());
om.configure(MapperFeature.USE_ANNOTATIONS, false);
om.configure(DeserializationFeature.FAIL_ON_UNKNOWN_PROPERTIES, false);
om.configure(SerializationFeature.FAIL_ON_EMPTY_BEANS, false);
om.activateDefaultTyping(LaissezFaireSubTypeValidator.instance
,ObjectMapper.DefaultTyping.NON_FINAL, JsonTypeInfo.As.PROPERTY);
om.setSerializationInclusion(JsonInclude.Include.NON_NULL);
serializer.setObjectMapper(om);
return redisTemplate;
}
}2.SpringDataRedis整合
<!--jedis-->
<dependency>
<groupId>redis.clients</groupId>
<artifactId>jedis</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--连接池依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.commons</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-pool2</artifactId>
</dependency>spring:
redis:
host: localhost
port: 6379
client-type: jedis
password: 123456
lettuce:
pool:
max-active: 16
max-idle: 8
min-idle: 0
max-wait: 100
jedis:
pool:
max-active: 16
@SpringBootTest
public class RedisTest{
// 以对象 操作的基本单元
// 客服端 : RedisTemplate 以对象作为Key 和 Value,内部对数据进行序列化 操作
@Autowired
private RedisTemplate redisTemplate;
@Test
public void setRedisTemplate(){
ValueOperations ops = redisTemplate.opsForValue();
ops.set("age",42);
Object age = redisTemplate.opsForValue().get("age");
System.out.println(age);
}
}@SpringBootTest
public class RedisTest{
// 以对象 操作的基本单元
// 客服端 : RedisTemplate 以对象作为Key 和 Value,内部对数据进行序列化 操作
@Autowired
private StringRedisTemplate stringRedisTemplate;
private static final ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper();
@Test
public void setAndGetRedisTemplate(){
stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().set("age",42);
Object age = stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().get("age");
User user = new User("Jack",21);
// 手动序列化
String JSON = mapper.writeValueAsString(user);
stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().set("user:1",JSON);
String jsonUser = stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().get("user:1");
User user1 = mapper.readValue(jsonUser,User.class);
System.out.print("user1"+user1);
}
}4.Axios
Axios是开源的在浏览器和Node.js的异步通信框架,她的主要作用就是实现AJAX异步通信
1.Axios特性
- 从浏览器中创建 XMLHttpRequests
- 从 node.js 创建 http 请求
- 支持 Promise API
- 拦截请求和响应
- 转换请求数据和响应数据
- 取消请求
- 自动转换 JSON 数据
- 客服端支持防御 XSRF(跨站请求伪渣)
5.redis课程笔记
2.Axios 使用
1.安装vue axios
1.下载 vue-axios
npm install --save axios vue-axios2.在main.js 引入
import Vue from 'vue'
import axios from 'axios'
import VueAxios from 'vue-axios'
Vue.use(VueAxios,axios)3.发送axios请求
import axios from "axios";
import Qs from 'qs'
methods: {
getData() {
const _this = this;
axios.get("http://localhost:8081/student/findAll").then(function (resp) {
console.log(response);
_this.tableData = resp.data;
})
}
}4.SpringMVC 解决跨域问题
<mvc:cors>
<mvc:mapping path="/**"
allowed-originPatterns="*"
allowed-methods="GET,POST,PUT,DELETE,OPTIONS,PATCH"
allow-credentials="true"
allowed-headers="Content-Type,Access-Control-Allow-Headers,Authorization,X-Requestes-With" />
</mvc:cors>1.解决axios无法传递data中的参数问题
默认情况下发送axios时请求头内容类型:
Content-Type:application/json;charset=UTF-8
实际服务端需要的:
Content-Type:application/x-www-form-urlencoded
因此,使用axios内置库中的方法进行内容类型的转换:
import Qs from 'qs'
this.axios({
method: 'post',
url: 'http://localhost:8081/reqist',
transformRequest: [function(data){
return Qs.stringify(data)
}],
data:{
email: this.email
}
})
.then(function(response){
alert(response.data.message)
});9.MyBatis入门
1.数据持久层框架
1.数据持久层
数据持久化指的将内存中的数据保存到磁盘中加以“固化”,几乎所有的应用系统都需要数据持久化。
持久化的实现通过将数据存储在各种关系型数据库中完成。
因此在应用框架中,一个相对独立的逻辑层,专注于数据持久化逻辑的实现,该逻辑层通常被称为“数据持久层”。
2.ORM
ORM一般指持久化数据和实现对象的映射。
ORM框架一般采用XML格式描述对象关系的映射细节,并且将其存放在专门的映射文件中。
2.Mybatis框架
Mybatis可以使用简单的XML代码或注解,将原生类型,接口和Jav的POJO配置映射为数据库中的记录。
MyBatis特点
1.简单易学
下载JAR包,配置SQL映射文件
2.灵活
SQl语句写在XML文件中,便于统一管理和优化。
解除SQL语句与程序代码的耦合,提供数据持久层,将业务逻辑和数据访问逻辑分离,使得系统设计更清晰,易维护,容易单元测试。
3.提供映射标签
支持对象和数据库的ORM字段关系映射,支持对象关系组建维护,提供XML标签,支持动态SQL。
相比较Hibernate设计理念完全面向POJO,MyBatis更适合网络性业务的灵活变化。
3.MyBatis工作原理
1.MyBatis核心类
1.Configuration
MyBatis的所有的配置信息都保存在Configuration对象中,XML配置文件中的大部分配置会存储在该类。
此外,提供设置配置信息的方法。Configuration可以从XML配置文件中获取属性值,也可以通过程序直接配置。
2.SqlSessionFactory
每个居于MyBtis的项目都通过SQL Session Factory的实列为中心
3.SqlSession
MyBatis的主要顶层API,SQL Session表示和数据库交互时的会话,完全包含面向数据库执行SQL语句所需要的所有方法。
SqlSession的实现类
1.DefaultSqlSession
2.SqlSessionManager
SqlSession通过内部存放的执行器(Executor)来对数据进行 CRUD 基础操作。
此外,每个线程都应该有自己的SQL Session实列,但SQL Session实列不是线程安全的,因此不能被共享,使用后需要关闭。
4.Executor
Executor是MyBatis的执行器,调度的核心,负责SQL语句的生成和查询缓存的维护。
5.MappedStatement
Mapped Statement对应配置文件中的 <select | update | delete | insert>节点,描述的是一条SQL语句。
2.MyBatis工作流程
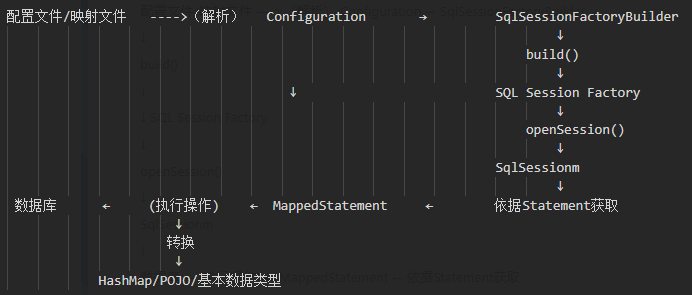
4.Mybatis入门
1.SQL
2.cn.edu.example.mybatis.mapper
StudentMapper.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<!-- namespace 表示命名空间 -->
<mapper namespace="cn.edu.example.mybatis.mapper.StudentMapper">
<!-- 根据学号获取学生信息-->
<select id="findStudentByStuno" parameterType="Integer"
resultType="cn.edu.example.mybatis.po.Student">
Select*from t_student where stuno=#{stuno}
</select>
</mapper>3.cn.edu.example.mybatis.po
Student.java
package cn.edu.example.mybatis.po;
public class Student {
private Integer stuno;// 主键,学号
private String stuname;// 学生姓名
private Integer grade;// 年纪
private String dept;// 专业
private String classname;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student [stuno=" + stuno + ", stuname=" + stuname + ", grade=" + grade + ", dept=" + dept
+ ", classname=" + classname + "]";
}
public Integer getStuno() {
return stuno;
}
public void setStuno(Integer stuno) {
this.stuno = stuno;
}
public String getStuname() {
return stuname;
}
public void setStuname(String stuname) {
this.stuname = stuname;
}
public Integer getGrade() {
return grade;
}
public void setGrade(Integer grade) {
this.grade = grade;
}
public String getDept() {
return dept;
}
public void setDept(String dept) {
this.dept = dept;
}
public String getClassname() {
return classname;
}
public void setClassname(String classname) {
this.classname = classname;
}
}3.cn.edu.example.mybatis.test
MyBatis.java
package cn.edu.example.mybatis.test;
import java.io.Reader;
import org.apache.ibatis.io.Resources;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactory;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactoryBuilder;
import cn.edu.example.mybatis.po.Student;
public class MybatisTest {
private static SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = null;
// 初始化SQL Session Factory对象
static {
try {
// 使用Mybatic提供的Resources类加载MyBatis的XML配置文件
Reader reader = Resources.getResourceAsReader("mybatis-config.xml");
// 构建SqlSessionFactory对象
// SqlSessionFactory对象
sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(reader);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
// 获取SQL Session对象的静态方法
public static SqlSession getSession() {
return sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
}
// 根据学号查询学生信息
public void findStudentByStunoTest() {
// 获取SQL Session
SqlSession sqlSession = getSession();
// Sqlsession 执行映射文件中定义的SQL语句,并返回映射结果
Student stu = sqlSession.selectOne("cn.edu.example.mybatis.mapper." + "StudentMapper.findStudentByStuno",
2018020222);
// 输出结果
System.out.println(stu.toString());
// 关闭SQL Session
sqlSession.close();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
MybatisTest test = new MybatisTest();
test.findStudentByStunoTest();
}
}4.mybatis-config.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE configuration PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd">
<configuration>
<!-- 配置环境,默认的环境ID为mysql-->
<environments default="mysql">
<!--配置环境ID为mysql的数据库环境 -->
<environment id="mysql">
<transactionManager type="JDBC"/>
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<property name="driver" value="com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver"/>
<property name="url"
value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis?serverTimezone=UTC"/>
<property name="username" value="root"/>
<property name="password" value="love1314"/>
</dataSource>
</environment>
</environments>
<!-- 配置映射器的位置-->
<mappers>
<mapper resource="cn/edu/example/mybatis/mapper/StudentMapper.xml"/>
</mappers>
</configuration>5.输出
Student [stuno=2018020222, stuname=����, grade=2018, dept=�����, classname=�����1802]
10 Mybatis配置
1.1 属性(properties)
properties 都是可以在外部配置且可以动态替换的,既可以在Java属性文件中配置,又可以在properties元素的子元素来传递。
1.2 设置(settings)
常用项目名 描述 有效值 默认值
cacheEnabled 全局地开启/关闭XML配置文件中的所有映射器已经配置的任何缓存 布尔值
multipleResultSetsEnabled 是/否允许单一语句返回多结果集
useColumnLabel 使用列表标签代替别名。不同的驱动会有不同的表现,具体可参考相
关驱动文档,或通过测试这两种不同的模式来观察所用驱动的结果。
useGeneratedKeys 允许JDBC支持自动化生成主键,需要驱动支持。如果设置为true,
则将强制使用自动生成主键。尽管一些驱动不支持此常用项。
autoMappbehavior 指定MyBatista应如何自动映射列到字段或属性上。
None表示取消自动映射;
Partial只会自动映射没有定义嵌套结果集映射的结果集;
full会自动映射任意复杂的结果集。
safeRowBoundsEnabled 允许在嵌套语句中使用分页(RowBounds)。如果允许使用,则设置
为 false
safeResultHandlerEnabled 允许在嵌套语句中使用分页(ResultHandler),如果使用设置为false。
returnlnstanceForEmptyRow 当返回的所有列是空时,MyBatis默认返回null。当开启这个设置时,
Mybatis会返回一个空实列。也适用于嵌套的结果集。
3.类型别名(typeAiases)
解释:
类型别名(typeAiases)是为Java数据类型设置一个短的名称。
只和XML配置文件有关,用来减少完全限定名的冗余。
1.
<typeAliases>
<typeAliase alias='Student' type='cn.edu.mybatis.po.Student' />
</typeAliases>Student 就可以在任何使用 cn.edu.mybatis.po.Student 的地方。
2.
<typeAliases>
<package name="cn.edu.mybatis.po" />
</typeAliases>
@Alias("Student")
public class Student{
...
}指定一个包名,Mybatis会在报名下搜索需要的JavaBean。
每一个在包 cn.edu.mybatis.po 中的JavaBean,在没有注解的情况下,都会使用 Bean 的首字母小写的非限定类名来作为她的别名。
4.环境配置(environments)
Mybatis可以配置多种环境,但是每一个 SqlSessionFactory实列只能对应一个环境。如果链接多个数据库,则需要创建多个 SqlSessionFactory实列。
为指定创建环境,需要将环境作为可选的参数传递给SQLSessionFactoryBuilder:
SqlSessionFactory factory =
new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(reader,environment[,properties]);当使用默认环境时:
SqlSessionFactory factory =
new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(reader[,properties]);1.元素定义配置环境
<environments default="del">
<environment id="del">
<transactionManager type="JDBC"></transactionManager>
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<!--Java 18 value="com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver"-->
<property name="driver" value="com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver"/>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis"/>
<property name="username" value="root"/>
<property name="password" value="love1314"/>
</dataSource>
</environment>
</environments>- (1). 默认使用的环境ID (default=“mysql”)
- (2). 每个environment元素定义的环境ID (id=”mysql”)
- (3). 事务管理器的配置(type=”JDBC”)
- (4). 数据源的配置 (type=”POOLED”)
1.事务管理器和数据源 介绍
1事务管理器 type=” [JDBC / MANAGED] “
- JDBC: 使用JDBC的提交和回滚设置,它依赖于从数据源得到的链接来管理事务作用域。
- MANAGED: 这个配置不提交或回滚一个链接,而是让容器来管理事物的整个生命周期。默认情况关闭连接,有些容器不希望如此,需要将closeConnection属性设置为false,来阻止默认的关闭操作。
- 使用 Mybatis和Spring不需要配置事务管理器,Spring自带管理器会覆盖配置。
2.数据源 type= “ [UNPOOLED / POOLED / JND ] “
虽然数据源的配置是可选的,但为使用延迟加载,数据源是必须配置的.
- UNPOOLED: 只用于每次请求时打开和关闭请求,适用于连接池不重要的。
- POOLED: 数据源利用“池”的概念将JDBC链接对象组织起来,避免创建新的链接实列时必须的初始化,节省认证时间。能使并发Web应用快速响应请求的处理方式,
- JNDI: 数据源实现为EJB或应用服务区这类容器中的使用,容器可以集中或在外部配置数据源并设置一个JNDI上下文的应用。
5.映射器(mappers)
相对于类似路径的资源应引用
<mappers>
<mapper resource="cn/edu/mybtis/mapper/SrudentMapper.xml" />
</mappers>
统一资源定位符
<mappers>
<mapper url="file:///var/mappers/SrudentMapper.xml" />
</mappers>
映射器接口实现类的完全限定类名
<mappers>
<mapper class="cn.edu.mybtis.mapper.SrudentMapper.xml" />
</mappers>
将包内的映射器接口实现全部注册为映射器
<mappers>
<package name="cn.edu.mybatis.mapper" />
</mappers>6. mapper.xml 常用SQL标签
<select id="selectByPrimaryKey" resultMap="BaseResultMap" parameterType="java.lang.String" >
selec...
</select> <insert id="insert" parameterType="pojo.OrderTable" >
insert into ordertable(...)
values(...)
</insert> <delete id="deleteByPrimaryKey" parameterType="java.lang.String" >
delete from ordertable
where order_id = #{orderId,jdbcType=VARCHAR}
</delete> <update id="updateByPrimaryKey" parameterType="pojo.OrderTable" >
update ordertable
set
cid = #{cid,jdbcType=VARCHAR},
address = #{address,jdbcType=VARCHAR},
create_date = #{createDate,jdbcType=TIMESTAMP},
orderitem_id = #{orderitemId,jdbcType=VARCHAR}
where
order_id = #{orderId,jdbcType=VARCHAR}
</update> <select id="listProduct" resultType="Product">
select * from product_
<if test="name!=null">
where name like concat('%',#{name},'%')
</if>
</select>1.需要配置的属性
1、id=”xxxx” 表示此段SQL执行语句的唯一标识,也是接口的方法名称 (必须一致才能找到)
2、parameterType=”xxxx” 表示SQL语句中需要传入的参数,类型要与对应的接口方法的类型一致
3、resultMap=”xxx” 定义出参,调用已定义的映射管理器的id的值
4、resultType=”xxxx” 定义出参,匹配普通Java类型或自定义的pojo (出参类型若不指定,将为语句类型默认类型,如语句返回值为int)
1.if 和 where 标签
<select id="listProduct" resultType="Product">
select * from product_
<where>
<if test="name!=null">
and name like concat('%',#{name},'%')
</if>
<if test="price!=null and price!=0">
and price > #{price}
</if>
</where>
</select>
/**
作用:
标签会进行自动判断:
如果任何条件都不成立,那么就在sql语句里就不会出现where关键字(重点)
如果有任何条件成立,会自动去掉多出来的 and 或者 or
*/2.set 标签
<update id="updateProduct" parameterType="Product" >
update product_
<set>
<if test="name != null">name=#{name},</if>
<if test="price != null">price=#{price}</if>
</set>
where id=#{id}
</update>
/**
作用:
标签会进行自动判断:
如果任何条件都不成立,那么就在sql语句里就不会出现where关键字(重点)
*/3.trim 标签
<select id="listProduct" resultType="Product">
select *from product_
<trim prefix="WHERE" prefixOverrides="AND |OR ">
<if test="name!=null">
and name like concat('%',#{name},'%')
</if>
<if test="price!=null and price!=0">
and price > #{price}
</if>
</trim>
</select>
<update id="updateProduct" parameterType="Product" >
update product_
<trim prefix="SET" suffixOverrides=",">
<if test="name != null">name=#{name},</if>
<if test="price != null">price=#{price}</if>
</trim>
where id=#{id}
</update>
/**
trim 用来定制想要的功能,比如where标签就可以用
*/4.chooseWhenOtherwise 标签
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.myjava.pojo">
<select id="listProduct" resultType="Product">
SELECT * FROM product_
<where>
<choose>
<when test="name != null">
and name like concat('%',#{name},'%')
</when>
<when test="price !=null and price != 0">
and price > #{price}
</when>
<otherwise>
and id >1
</otherwise>
</choose>
</where>
</select>
</mapper>
/**
有任何任何条件符合,就进行条件查询,否则就只使用id>1这个条件
*/5.foreach 标签
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.myjava.pojo">
<select id="listProduct" resultType="Product">
SELECT * FROM product_
WHERE ID in
<foreach item="item" index="index" collection="list"
open="(" separator="," close=")">
#{item}
</foreach>
</select>
</mapper>6.bind 标签
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.myjava.pojo">
<select id="listProduct" resultType="Product">
<bind name="likename" value="'%' + name + '%'" />
select * from product_ where name like #{likename}
</select>
</mapper>7.sql 片段标签
<!--定义sql片段-->
<sql id="orderAndItem">
o.order_id,o.cid,o.address,o.create_date,o.orderitem_id,i.orderitem_id,i.product_id,i.count
</sql>
<select id="findOrderAndItemsByOid" parameterType="java.lang.String" resultMap="BaseResultMap">
select <!--引用sql片段-->
<include refid="orderAndItem" />
from
ordertable o
join orderitem i
on o.orderitem_id = i.orderitem_id
where
o.order_id = #{orderId}
</select>
/**
作用是:
通过该标签可定义能复用的sql语句片段,在执行sql语句标签中直接引用即可。
这样既可以提高编码效率,还能有效简化代码,提高可读性。
*/7. Mybatis 多表查询
1. 一对一
<sql id="ListMap">
b.id,b.productName,p.proName,b.totalPrice,b.isPayment,b.creationDate
</sql>
/**
resultMap: 声明 一个存储多个POJO 对象的图表
property: pojo 对象属性
column: mysql 列名
*/
<resultMap id="toProviderId" type="top.wabisabifag.entity.SmbmsBill">
<id property="id" column="id"/>
<result property="productName" column="productName"/>
<result property="totalPrice" column="totalPrice"/>
<result property="isPayment" column="isPayment"/>
<result property="creationDate" column="creationDate"/>
<!-- 相同列名的做区分-->
<association property="smbmsProvider" javaType="top.wabisabifag.entity.SmbmsProvider">
<result property="proName" column="proName"/>
</association>
</resultMap>
/**
resultMap: 使用声明的图表
*/
<select id="billShowList" resultMap="toProviderId">
select <include refid="ListMap" />
from smbms_bill b, smbms_provider p
where b.providerId = p.id
</select>private SmbmsProvider smbmsProvider;2. 一对多
<sql id="ListMap">
b.id,b.productName,p.proName,b.totalPrice,b.isPayment,b.creationDate
</sql>
/**
resultMap: id="toProviderId" 声明 一个存储多个POJO 对象的图表
property: pojo 对象属性
column: mysql 列名
*/
<resultMap id="toProviderId" type="top.wabisabifag.entity.SmbmsBill">
<id property="id" column="id"/>
<result property="productName" column="productName"/>
<result property="totalPrice" column="totalPrice"/>
<result property="isPayment" column="isPayment"/>
<result property="creationDate" column="creationDate"/>
<!-- 配置集合信息
property: 集合在POJO对象的名称
ofType:当前集合中的数据类型
-->
<collection property="smbmsProviderList" ofType="top.wabisabifag.entity.SmbmsProvider">
<result property="proName" column="proName"/>
</collection>
</resultMap>
/**
resultMap = "toProviderId" 使用声明的图表
*/
<select id="billShowList" resultMap="toProviderId">
select <include refid="ListMap" />
from smbms_bill b, smbms_provider p
where b.providerId = p.id
</select>private List<SmbmsProvider> smbmsProviderList;3. 多对多
<resultMap id="userRoleMap" type="user">
/* user 信息 */
<id column="userId" property="id"/>
<result column="username" property="username"/>
<result column="password" property="password"/>
<result column="birthday" property="birthday"/>
<collection property="roleList" ofType="top.wabisabifag.entity.role">
/* user内部roleList 信息 */
<id property="id" cloumn="roleId"/>
<result property="roleName" column="roleName"/>
<result property="roleDesc" column="roleDesc"/>
</collection>
</resultMap>
<select id="findUserAndRoleAll" resultMap="userRoleMap">
select * from user u,
sys_user_role ur,
sys_role r
where
u.id=ur.userTd and ur.roleId=r.id
</select>三张表,中间表进行连接作用,仅在查询语句时作用
面试题
Mybatis
- mybatis
1.一级缓存
mapper调用对象代理的session,对数据库查询数据后会存在的数据缓存。
出现的问题:
当在同一个方法中连贯query的时候,由于代码非 mapper代理绑定在前一个mapper对象上,会报错。
解决方法:
再次赋值绑定到mapper的session上进行query。
2.二级缓存
(1)为什么有二级缓存:
一级缓存,查询的数据不是数据库的数据,而是直接在Client端发送request请求给Tomcat,在服务器同一个线程的缓存中调用,该线程第二次调用时不访问数据库。
(2)二级缓存的存在原理:
二级缓存会重新独立访问数据库,以便获取最新的数据库信息。
出现的问题:
(1)由于Spring不对外开放,mybatis二级缓存会自动关闭对数据库的访问。
(2)当数据操作的方法联动(动态)改动信息的时候,无法获得改动的最新数据。
Spring —黑马程序员
Spring
思想:
IoC ( inversion of Control) ,控制反转,强调的是原来在程序中创建Bean的权利反转给第三方。Spring接管操纵。
DI (Dependency Injection),依赖注入,强调的bean之间关系,这种关系第三方负责设置。
AOP (Aspect Oriented Programming),面向切面编程。功能的横向抽取,主要的实现方式就是 Peoxy。Spring提供:
IoC,AOP,Web MVCSpring Frameworl技术栈:
Data Access:数据访问
Data Integration:数据集成
Web:Web开发
ADP:面向切面编程
Aspects:AOP思想实现
Core Container:核心容器
Test:单元测试,集成测试BeanFactory与ApplicationContext的关系:
1.BeanFactory时Spring的早期接口,称为Spring的Bean工厂,Application Context时后期更高级的接口,是Spring容器;
2.Application Context早Bean Factory基础上对功能进行了扩展,列如:监听功能,国际化功能等。Bean Factory的API更偏向底层,Application Context的API多数是对底层API的封装;
3.Bean的创建主要逻辑和功能都被封装在Bean Factory中,Application Context不仅继承Bean Factory,而且Application Context内部还维护着Bean Factory的引用,所以,ApplicationContext与Bean Factory既有继承关系,又有任何关系;
4.bean的初始化实际不同,原始Bean Factory是在首次调用个体Bean是才进行Bean的创建,而Application Context则是配置文件加载,容器一创建就将Bean都实列化并初始化好;
基于xml的Spring应用
SpringBean 的配置详解
xml配置方式 功能描述
<bean id="" class=""> 全限定名配置
<bean name=""> 通过name设置Bean的别名,通过别名也能直接获取到Bean实列
<bean scope=""> Bean的作用范围,Bean Factory作为容器时取值singleton和prototype
<bean lazy-init=""> Bean实列化时机,是否延迟加载。Bean Factory作为容器时无效
<bean init-method=""> Bean的实列化后自动执行的初始化方法,method指定方法名
<bean destory-method=""> Bean实列销毁钱的方法,method指定方法名
<bean autowire="byType"> 设置自动注入模式,常用的有按照类型byType,按照名字byName
<bean factory-bean="" factory-method=""/> 指定那个工厂Bean的那个方法完成Bean的创建SpringBean配置
<!-- 配置UserServiceImpl-->
<bean id="userService" class="top.wabisabifag.service.impl.UserServiceImpl">
<property name="userDao" ref="userDao"></property>
</bean>
<!-- 篇日志UserDaoImpl-->
<bean id="userDao" class="top.wabisabifag.service.impl.UserDaoImpl"></bean>Bean的基础配置
列如:
配置UserDaoImpl由Spring容器负责管理
此时存储到Spring容器的Bean的beanName时uerDao,值是UserDaoImpl对象,可根据beanName获取Bean实列
applicationContext.getBean(“userDao”);
如不配置id,则Spring会把当前Bean实列的全限定名作为beanName
applicationContext.getBean(“top.wabisabifag.dao.impl.UserDaoImpl”)Bean的别名配置
可以为当前Bean指定多个别名,根据别名可获得Bean对象
此时多个名称可以获得UserDaoImpl实列duixiang
applicationContext.getBean(“UserDao”);
applicationContext.getBean(“aa”);
applicationContext.getBean(“bb”);Bean的范围设置
单纯的Spring环境的作用有两个:Singleton和Prototype
Singleton:单列,默认值,Spring容器创建时候就会进行Bean的实列化,并存储到容器内部的单列池中,每次getBean时都是从单列池中获取相同的Bean实列
prototype:原型,Spring容器初始化时不会创建Bean实列,当调用getBean时才会实列化Bean,每次getBean都会创建一个新的Bean实列Bean的延迟加载
当lazy-init设置为true,Spring容器创建时不会立即创建Bean实列,等待用到时在创建Bean实列并存储到单列池中,后续在使用该Bean直接从单列池获取,本质上该Bean还是单列
Bean的初始化和销毁方法配置
Bean在被实列化后,可执行指定的初始化方法完成一些初始化的操作,Bean在销毁之前也可以执行指定的销毁方法完成一些操作,初始化方法名称和销毁方法名称通过
<bean id="userDao" class="top.wabisabifag.dao.impl.UserDaoImpl" init-method="init" destory-method="destroy"/> public class UserDaoImpl implements UserDao{ public UserDaoImpl(){}; public void init(){}; public void destory(){}; }Bean的实列化配置
Spring的实列化方式:构造方式实列化:底层通过构造方法对Bean进行实列化
<!-- 配置UserServiceImpl--> <bean id="userService" class="top.wabisabifag.service.impl.UserServiceImpl"> <!-- UserDapImpl的有参构造--> <constructor-arg name="name" value="H"></constructor> <property name="userDao" ref="userDao"></property> </bean> <!-- 篇日志UserDaoImpl--> <bean id="userDao" class="top.wabisabifag.service.impl.UserDaoImpl"></bean>工厂方式实列化:底层通过调用自定义的工厂方式对Bean进行实列化
静态工厂方法实列化Bean
id定义一个在impl.UserServiceImpl函数方法下的 userDao 函数方法.
可以被应用,便于在运行前在该方法中的其他功能的运行调用.
<!-- 配置UserServiceImpl--> <bean id="user" class="top.wabisabifag.service.impl.UserServiceImpl" factory-method="userDao"></bean>实列工厂方法实列化Bean
实现FavtoryBean规范延迟实列化Bean
2.Spring 的get方法
3.Spring 配置非定义Bean
4,Bean 实列化的基本流程
5.Spring 的后处理器
6.SpringBean 的生命周期
7.Spring Ioc 整体流程总结
8.Spring xml 方式整合第三方框架